python实现图像风格转化-人工智能图像处理
什么是图像风格转换?如上图可见,一键变成艺术大师。所谓图片风格迁移,是指利用程序算法学习著名画作的风格,然后再把这种风格应用到另外一张图片上的技术。基本原理如下图可见:我们知道,卷积神经网络(CNN)具有很强的图像特征(feature/representation)提取能力,如上图所示。对于内容图片,深层网络(d和e)提取的是高维特征,同时也丢弃了细节信息;浅层网络(a, b和c)提...
·
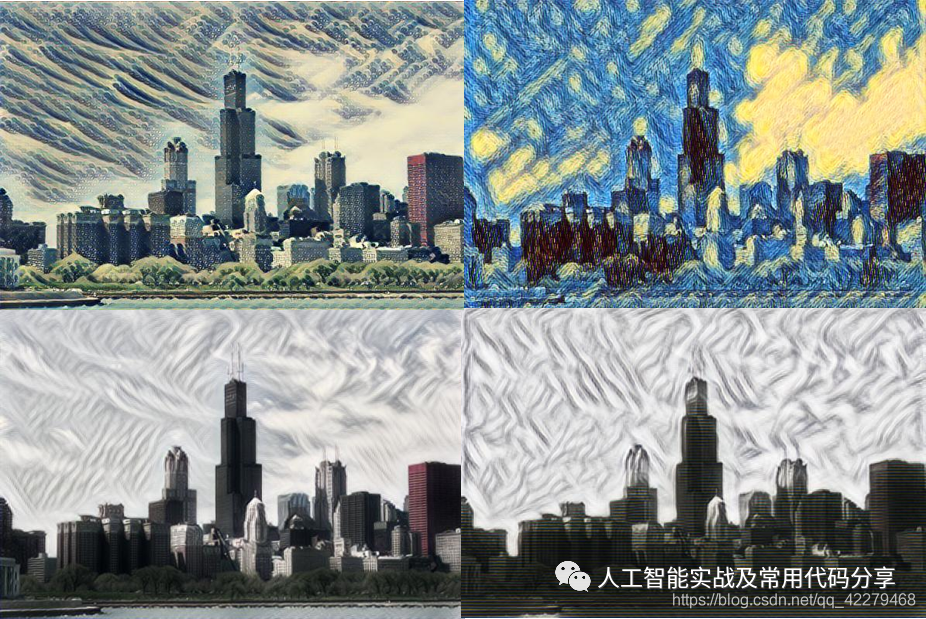
什么是图像风格转换?如上图可见,一键变成艺术大师。
所谓图片风格迁移,是指利用程序算法学习著名画作的风格,然后再把这种风格应用到另外一张图片上的技术。
基本原理
如下图可见: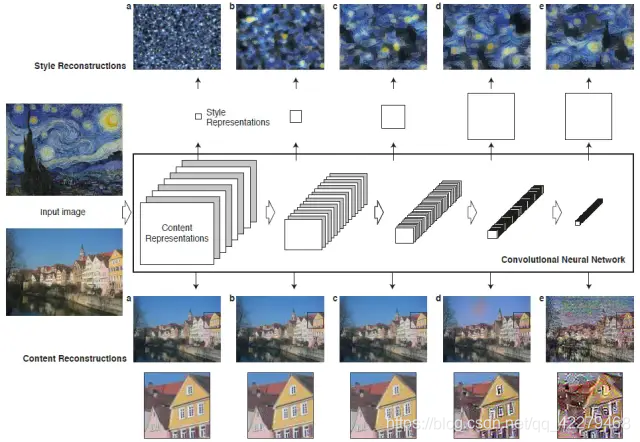
我们知道,卷积神经网络(CNN)具有很强的图像特征(feature/representation)提取能力,如上图所示。
对于内容图片,深层网络(d和e)提取的是高维特征,同时也丢弃了细节信息;浅层网络(a, b和c)提取的是低维特征,图片的细节大多都保留下来了。
对于风格图片,通过包含多层的特征相关性(Gram矩阵),可获得多尺度图像风格的重构,捕获其纹理信息。这样构建的网络可以忽略图像的具体细节,保留风格。
为了将内容图片和风格图片融合在一起(见下图),我们应该使风格化结果图(初始为一张白噪声图片)的特征同时与内容图片和风格图片的特征之间的距离最小化,最终获取我们所需的风格化结果图。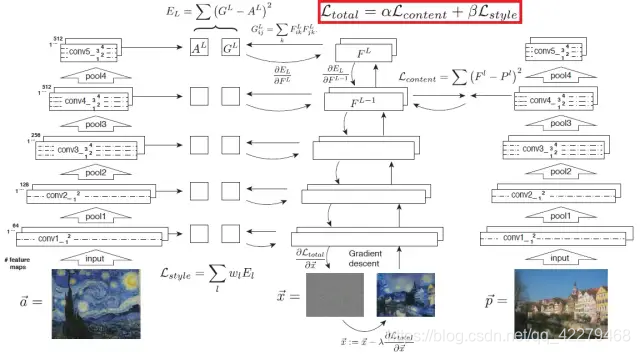
代码:
# coding = utf-8
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
slim = tf.contrib.slim
def arg_scope(weight_decay=0.0005):
with slim.arg_scope([slim.conv2d, slim.fully_connected, slim.conv2d_transpose],
activation_fn=None,
weights_regularizer=slim.l2_regularizer(weight_decay),
biases_initializer=tf.zeros_initializer()):
with slim.arg_scope([slim.conv2d, slim.conv2d_transpose], padding='SAME') as arg_sc:
return arg_sc
def img_scale(x, scale):
weight = x.get_shape()[1].value
height = x.get_shape()[2].value
try:
out = tf.image.resize_nearest_neighbor(x, size=(weight*scale, height*scale))
except:
out = tf.image.resize_images(x, size=[weight*scale, height*scale])
return out
# net = slim.conv2d(net, 4096, [1, 1], scope='fc7')
def res_module(x, outchannel, name):
with tf.variable_scope(name_or_scope=name):
out1 = slim.conv2d(x, outchannel, [3, 3], stride=1, scope='conv1')
out1 = relu(out1)
out2 = slim.conv2d(out1, outchannel, [3, 3], stride=1, scope='conv2')
out2 = relu(out2)
return x+out2
def instance_norm(x):
epsilon = 1e-9
mean, var = tf.nn.moments(x, [1, 2], keep_dims=True)
return tf.div(tf.subtract(x, mean), tf.sqrt(tf.add(var, epsilon)))
def relu(x):
return tf.nn.relu(x)
def gen_net(imgs, reuse, name, is_train=True):
imgs_shape = tf.shape(imgs)
imgs = tf.pad(imgs, [[0, 0], [10, 10], [10, 10], [0, 0]], mode='REFLECT')
with tf.variable_scope(name, reuse=reuse) as vs:
# encoder : three convs layers
out1 = slim.conv2d(imgs, 32, [9, 9], scope='conv1')
out1 = relu(instance_norm(out1))
out2 = slim.conv2d(out1, 64, [3, 3], stride=2, scope='conv2')
out2 = instance_norm(out2)
# out2 = relu(img_scale(out2, 0.5))
out2 = slim.conv2d(out2, 128, [3, 3], stride=2, scope='conv3')
out2 = instance_norm(out2)
# out2 = relu(img_scale(out2, 0.5))
# transform
out3 = res_module(out2, 128, name='residual1')
out3 = res_module(out3, 128, name='residual2')
out3 = res_module(out3, 128, name='residual3')
out3 = res_module(out3, 128, name='residual4')
# decoder
out4 = img_scale(out3, 2)
out4 = slim.conv2d(out4, 64, [3, 3], stride=1, scope='conv4')
out4 = relu(instance_norm(out4))
# out4 = img_scale(out4, 128)
out4 = img_scale(out4, 2)
out4 = slim.conv2d(out4, 32, [3, 3], stride=1, scope='conv5')
out4 = relu(instance_norm(out4))
# out4 = img_scale(out4, 256)
out = slim.conv2d(out4, 3, [9, 9], scope='conv6')
out = tf.nn.tanh(instance_norm(out))
variables = tf.contrib.framework.get_variables(vs)
out = (out + 1) * 127.5
height = out.get_shape()[1].value # if is_train else tf.shape(out)[0]
width = out.get_shape()[2].value # if is_train else tf.shape(out)[1]
# out = tf.slice(out, [0, 10, 10, 0], tf.stack([-1, height - 20, width - 20, -1]))
out = tf.image.crop_to_bounding_box(out, 10, 10, height-20, width-20)
# out = tf.reshape(out, imgs_shape)
return out, variables
"""caculate the loss"""
import vgg_simple as vgg
import os
def styleloss(f1, f2, f3, f4):
gen_f, _, style_f = tf.split(f1, 3, 0)
size = tf.size(gen_f)
style_loss = tf.nn.l2_loss(gram(gen_f) - gram(style_f))*2 / tf.to_float(size)
gen_f, _, style_f = tf.split(f2, 3, 0)
size = tf.size(gen_f)
style_loss += tf.nn.l2_loss(gram(gen_f) - gram(style_f)) * 2 / tf.to_float(size)
gen_f, _, style_f = tf.split(f3, 3, 0)
size = tf.size(gen_f)
style_loss += tf.nn.l2_loss(gram(gen_f) - gram(style_f)) * 2 / tf.to_float(size)
gen_f, _, style_f = tf.split(f4, 3, 0)
size = tf.size(gen_f)
style_loss += tf.nn.l2_loss(gram(gen_f) - gram(style_f)) * 2 / tf.to_float(size)
return style_loss
def gram(layer):
shape = tf.shape(layer)
num_images = shape[0]
width = shape[1]
height = shape[2]
num_filters = shape[3]
filters = tf.reshape(layer, tf.stack([num_images, -1, num_filters]))
grams = tf.matmul(filters, filters, transpose_a=True) / tf.to_float(width * height * num_filters)
return grams
if __name__ == '__main__':
with tf.device('/cpu:0'):
a = [[1., 2.], [3., 4.], [5, 6]]
b, c, e = tf.split(a, 3, 0)
with tf.Session() as sess:
c, d, g = sess.run([b, c, e])
完整模型、训练和转化代码,关注公众号“人工智能实战及常见代码分享”,后台回复“风格迁移”获取
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献2条内容
已为社区贡献2条内容









所有评论(0)