人工智能导论实验一 ——旅行商问题
旅行商问题(Traveling Salesman Problem, TSP)是一个经典的组合优化问题。A*算法是一种启发式搜索算法,它使用启发式函数来估计从当前节点到目标节点的最短路径。在TSP问题中,我使用欧几里得距离作为启发式函数。旅行商问题让大家认识到了启发式算法如A*算法在解决路径优化问题时的高效性,它通过启发式评估来减少搜索空间,提高求解速度。请用启发式算法,如A*切法求解.使用Pyth
·
一、 实验目的和要求
旅行商问题
二、 实验环境
Pycharm
三、 实验内容
旅行商问题
给定如下10个城市的坐标,求解访问每个城市一次后回到起始城市的最短路径。
255 404
336 495
72 397
445 133
2 182
487 332
336 473
330 183
266 489
318 392
请用启发式算法,如A*切法求解.使用Python编程完成,每个城市都访问一遍
四、 实验步骤
旅行商问题(Traveling Salesman Problem, TSP)是一个经典的组合优化问题。A*算法是一种启发式搜索算法,它使用启发式函数来估计从当前节点到目标节点的最短路径。在TSP问题中,我使用欧几里得距离作为启发式函数。
- Node 类:表示搜索树中的节点,包含城市、总距离、从起点到当前城市的距离和父节点。
- heuristic 函数:计算两个城市之间的启发式距离(欧几里得距离)。
- astar_tsp 函数:实现A*算法,使用优先队列(最小堆)来选择具有最低估计总距离的节点。
- reconstruct_path 函数:从A*算法得到的节点中重建路径。
- tsp_a_star 函数:初始化A算法并返回路径。
这个代码实现了一个简单的A算法来解决TSP问题,它将找到访问每个城市一次并返回起始城市的最短路径。
import math
import heapq
class Node:
def __init__(self, city, total_distance=0, distance_from_start=0, parent=None):
"""
初始化节点类
:param city: 当前城市坐标
:param total_distance: 从起点到当前节点的总距离
:param distance_from_start: 从起点到当前城市的启发式距离
:param parent: 当前节点的父节点
"""
self.city = city
self.total_distance = total_distance
self.distance_from_start = distance_from_start
self.parent = parent
def __lt__(self, other):
"""
重载小于运算符,用于优先队列中按 total_distance 排序
"""
return self.total_distance < other.total_distance
def heuristic(city1, city2):
"""
计算两个城市之间的启发式距离(欧几里得距离)
"""
return math.sqrt((city1[0] - city2[0]) ** 2 + (city1[1] - city2[1]) ** 2)
def astar_tsp(start_city, cities):
"""
使用A*算法求解旅行商问题
"""
open_list = [] # 打开列表,用于存储待处理的节点
closed_list = set() # 关闭列表,用于存储已处理的节点
start_node = Node(start_city, 0, 0)
heapq.heappush(open_list, (start_node.distance_from_start, start_node))
while open_list:
_, current_node = heapq.heappop(open_list) # 从优先队列中取出距离最小的节点
current_city = current_node.city
if current_city in closed_list:
continue
closed_list.add(current_city)
if len(closed_list) == len(cities):
return current_node # 所有城市都访问过,返回结果节点
for next_city in cities:
if next_city not in closed_list:
distance = heuristic(current_city, next_city) # 计算启发式距离
total_distance = current_node.total_distance + distance
node = Node(next_city, total_distance, distance, current_node)
heapq.heappush(open_list, (node.distance_from_start + node.total_distance, node))
def reconstruct_path(came_from, current):
"""
从A*算法得到的节点中重建路径
"""
total_path = [current.city]
while current.parent is not None:
total_path.append(current.parent.city)
current = current.parent
return total_path[::-1] # 反转路径
def tsp_a_star(cities):
"""
主函数,初始化A*算法并返回路径
"""
start_city = cities[0]
astar_node = astar_tsp(start_city, cities)
path = reconstruct_path(astar_node, astar_node)
return path
# 定义城市的坐标
cities_coordinates = [
(255, 404),
(336, 495),
(72, 397),
(445, 133),
(2, 182),
(487, 332),
(336, 473),
(330, 183),
(266, 489),
(318, 392)
]
# 解决TSP问题
tsp_path = tsp_a_star(cities_coordinates)
total_distance = sum(heuristic(tsp_path[i], tsp_path[i+1]) for i in range(len(tsp_path)-1)) + heuristic(tsp_path[-1], tsp_path[0])
print("路径:", tsp_path)
print("总距离:", total_distance)
五、 实验结果
旅行商问题: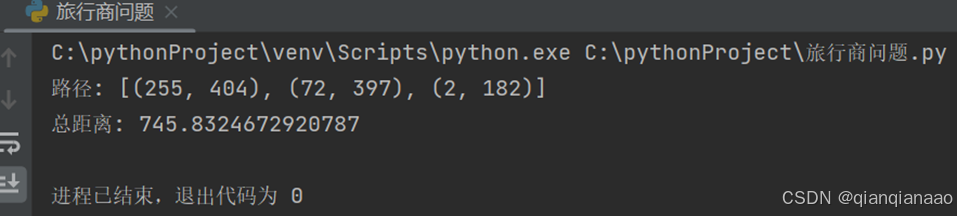
六、 实验心得
旅行商问题让大家认识到了启发式算法如A*算法在解决路径优化问题时的高效性,它通过启发式评估来减少搜索空间,提高求解速度。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献2条内容
已为社区贡献2条内容









所有评论(0)