Python 运维脚本
【代码】Python 运维脚本。
·
1、备份文件
import os
import shutil
# 定义配置文件目录和备份目录的路径
config_dir = "/root/python/to/config/files/"
backup_dir = "/root/python/to/backup/"
# 遍历配置文件目录中的所有文件
for filename in os.listdir(config_dir):
# 如果文件名以 ".conf" 结尾,则执行备份操作
if filename.endswith('.conf'):
# 构建完整的文件路径
file_path = os.path.join(config_dir, filename)
# 构建备份文件路径
backup_path = os.path.join(backup_dir, filename)
# 将文件复制到备份目录
shutil.copy(file_path, backup_path)
# 打印备份完成的消息
print(f"Backup of {filename} completed")
2、安装pip
- 根据不同的版本,安装不同的pip
wget https://bootstrap.pypa.io/pip/3.6/get-pip.py
python3 get-pip.py

3、将备份文件传送到远程主机上进行备份
import os
import shutil
import paramiko
# 定义配置
local_config_dir = "/root/python/to/config/files/"
remote_backup_dir = "/root/python/to/backup/"
remote_host = "192.168.1.101"
remote_username = "root" # 根据实际情况修改用户名
remote_password = "your_password" # 根据实际情况修改密码
# 检查本地配置目录是否存在
if not os.path.exists(local_config_dir):
print(f"Local directory {local_config_dir} does not exist.")
exit(1)
# 创建一个 SSH 客户端对象
ssh = paramiko.SSHClient()
ssh.set_missing_host_key_policy(paramiko.AutoAddPolicy())
try:
# 连接远程服务器
print(f"Connecting to {remote_host}...")
ssh.connect(remote_host, username=remote_username, password=remote_password)
# 创建一个 SFTP 客户端对象
sftp = ssh.open_sftp()
# 检查远程目录是否存在,如果不存在则创建
print(f"Checking remote directory {remote_backup_dir}...")
try:
sftp.stat(remote_backup_dir)
print(f"Directory {remote_backup_dir} already exists.")
except IOError:
print(f"Directory {remote_backup_dir} does not exist. Creating...")
sftp.mkdir(remote_backup_dir)
# 遍历本地目录中的所有文件
for filename in os.listdir(local_config_dir):
file_path = os.path.join(local_config_dir, filename)
backup_path = os.path.join(remote_backup_dir, filename)
# 检查是否为文件(忽略目录)
if os.path.isfile(file_path):
print(f"Transferring {file_path} to {backup_path}...")
sftp.put(file_path, backup_path)
print(f"Transfer of {filename} completed.")
finally:
# 关闭 SFTP 和 SSH 连接
print("Closing SSH connection...")
ssh.close()
4、对历史日志进行删除
## 日志保留策略
import os
import time
# 日志文件所在的目录
log_dir = '/path/to/logs/'
# 文件的最大保留天数
days_old = 30
# 获取当前时间戳
current_time = time.time()
# 遍历日志目录中的所有文件
for filename in os.listdir(log_dir):
# 构造文件的完整路径
file_path = os.path.join(log_dir, filename)
# 计算文件的年龄(以秒为单位)
file_age = current_time - os.path.getmtime(file_path)
# 如果文件年龄超过最大保留天数(以秒为单位),则删除该文件
if file_age > days_old * 86400:
os.remove(file_path)
print(f"Deleted old log file: {filename}")
5、查看模块是否安装
import importlib
import sys # 用于处理命令行参数
def check_modules(modules):
"""检查指定的模块是否已安装"""
for module_name in modules:
try:
importlib.import_module(module_name)
print(f"{module_name} is installed.")
except ImportError:
print(f"{module_name} is not installed.")
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 通过命令行参数获取模块名称列表
if len(sys.argv) < 2:
print("Usage: python script.py module1 module2 ...")
sys.exit(1)
# 从命令行参数中提取模块名称
modules = sys.argv[1:]
# 检查模块是否已安装
check_modules(modules)
- 脚本使用:
python3 test1.py time os

6、 查看系统进程
##获取当前所有的进程
import psutil
# 遍历所有进程,获取进程的 PID 和名称
for proc in psutil.process_iter(['pid', 'name']):
# 打印每个进程的 PID 和名称
print(f"PID: {proc.info['pid']}, 进程名: {proc.info['name']}")
7、系统资源监控
1、只监控挂载点
import psutil
def get_disk_usage():
partitions = psutil.disk_partitions()
for partition in partitions:
usage = psutil.disk_usage(partition.mountpoint)
total_gb = usage.total / (2**30) # 转换为 GiB
used_gb = usage.used / (2**30) # 转换为 GiB
free_gb = usage.free / (2**30) # 转换为 GiB
print(f"挂载点: {partition.mountpoint}")
print(f"总空间: {total_gb:.2f} GiB")
print(f"已用空间: {used_gb:.2f} GiB")
print(f"剩余空间: {free_gb:.2f} GiB")
print("-" * 30)
# 调用函数
get_disk_usage()
2、全部挂载点都监控
import psutil
def get_disk_usage(mountpoints):
for mountpoint in mountpoints:
try:
usage = psutil.disk_usage(mountpoint)
total_gb = usage.total / (2**30) # 转换为 GiB
used_gb = usage.used / (2**30) # 转换为 GiB
free_gb = usage.free / (2**30) # 转换为 GiB
print(f"挂载点: {mountpoint}")
print(f"总空间: {total_gb:.2f} GiB")
print(f"已用空间: {used_gb:.2f} GiB")
print(f"剩余空间: {free_gb:.2f} GiB")
print("-" * 30)
except Exception as e:
print(f"分析挂载点 {mountpoint} 出错: {e}")
# 手动指定要分析的挂载点
mountpoints = [
'/', # 根目录
'/boot', # 启动分区
'/dev', # 设备文件挂载点
'/tmp', # 临时文件系统
'/run', # 用于运行时数据
'/var/lib/docker/overlay2', # Docker 的 overlayfs 挂载点
'/sys/fs/cgroup', # cgroup 文件系统
'/proc', # proc 文件系统
'/sys', # 系统文件
'/mnt' # 用户指定的挂载点示例
]
# 调用函数
get_disk_usage(mountpoints)
3、CPU 内存 磁盘监控
import datetime
import psutil
import shutil
def get_system_report():
report = []
# 报告生成时间
report.append(f"报告生成时间: {datetime.datetime.now().strftime('%m-%d')}")
# CPU使用率
report.append(f"CPU使用率: {psutil.cpu_percent()}%")
# 内存使用率
report.append(f"内存使用率: {psutil.virtual_memory().percent}%")
# 磁盘使用情况
total, used, free = shutil.disk_usage("/")
report.append(f"磁盘总空间: {total // (2**30)}GiB")
report.append(f"磁盘已用空间: {used // (2**30)}GiB")
report.append(f"磁盘剩余空间: {free // (2**30)}GiB")
# 返回拼接的报告
return "\n".join(report)
# 打印系统报告
print(get_system_report())
8、用户管理
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import os
import sys
import pwd
import grp
import subprocess
from typing import List, Optional
from rich.console import Console
from rich.table import Table
from rich.prompt import Prompt, Confirm
from rich.panel import Panel
from rich import print as rprint
console = Console()
class UserManager:
def __init__(self):
self.console = Console()
self.check_root_privileges()
self.sudoers_file = "/etc/sudoers"
self.sudoers_dir = "/etc/sudoers.d"
def check_root_privileges(self):
"""检查是否具有root权限"""
if os.geteuid() != 0:
self.console.print("[red]错误:此程序需要root权限才能运行![/red]")
self.console.print("请使用 sudo 运行此程序")
sys.exit(1)
def run_command(self, command: List[str]) -> tuple:
"""执行shell命令"""
try:
result = subprocess.run(
command,
stdout=subprocess.PIPE,
stderr=subprocess.PIPE,
universal_newlines=True,
check=True
)
return True, result.stdout
except subprocess.CalledProcessError as e:
return False, e.stderr
def list_users(self):
"""列出所有用户"""
table = Table(title="系统用户列表")
table.add_column("用户名", style="cyan")
table.add_column("UID", style="green")
table.add_column("GID", style="yellow")
table.add_column("主目录", style="blue")
table.add_column("Shell", style="magenta")
for user in pwd.getpwall():
table.add_row(
user.pw_name,
str(user.pw_uid),
str(user.pw_gid),
user.pw_dir,
user.pw_shell
)
self.console.print(table)
def create_user(self):
"""创建新用户"""
try:
username = Prompt.ask("请输入新用户名")
# 检查用户是否已存在
try:
pwd.getpwnam(username)
self.console.print(f"[red]错误:用户 {username} 已存在![/red]")
return
except KeyError:
pass
# 获取用户信息
home_dir = Prompt.ask("请输入主目录", default=f"/home/{username}")
shell = Prompt.ask("请输入shell", default="/bin/bash")
create_home = Confirm.ask("是否创建主目录?", default=True)
set_password = Confirm.ask("是否设置密码?", default=True)
# 构建useradd命令
cmd = ["useradd"]
if create_home:
cmd.append("-m")
cmd.extend(["-d", home_dir, "-s", shell, username])
success, output = self.run_command(cmd)
if success:
self.console.print(f"[green]成功创建用户 {username}[/green]")
if set_password:
self.set_password(username)
else:
self.console.print(f"[red]创建用户失败:{output}[/red]")
except KeyboardInterrupt:
self.console.print("\n[yellow]已取消创建用户[/yellow]")
def delete_user(self):
"""删除用户"""
username = Prompt.ask("请输入要删除的用户名")
# 检查用户是否存在
try:
pwd.getpwnam(username)
except KeyError:
self.console.print(f"[red]错误:用户 {username} 不存在![/red]")
return
remove_home = Confirm.ask("是否删除用户主目录?", default=True)
cmd = ["userdel"]
if remove_home:
cmd.append("-r")
cmd.append(username)
success, output = self.run_command(cmd)
if success:
self.console.print(f"[green]成功删除用户 {username}[/green]")
else:
self.console.print(f"[red]删除用户失败:{output}[/red]")
def set_password(self, username: Optional[str] = None):
"""设置用户密码"""
try:
if username is None:
username = Prompt.ask("请输入用户名")
# 检查用户是否存在
try:
pwd.getpwnam(username)
except KeyError:
self.console.print(f"[red]错误:用户 {username} 不存在![/red]")
return
# 使用chpasswd命令设置密码
password = Prompt.ask("请输入新密码", password=True)
confirm_password = Prompt.ask("请再次输入密码", password=True)
if password != confirm_password:
self.console.print("[red]错误:两次输入的密码不一致![/red]")
return
# 使用echo和chpasswd命令设置密码
cmd = f"echo '{username}:{password}' | chpasswd"
success, output = self.run_command(["bash", "-c", cmd])
if success:
self.console.print(f"[green]成功设置用户 {username} 的密码[/green]")
else:
self.console.print(f"[red]设置密码失败:{output}[/red]")
except KeyboardInterrupt:
self.console.print("\n[yellow]已取消设置密码[/yellow]")
def modify_user(self):
"""修改用户信息"""
try:
username = Prompt.ask("请输入要修改的用户名")
# 检查用户是否存在
try:
user_info = pwd.getpwnam(username)
except KeyError:
self.console.print(f"[red]错误:用户 {username} 不存在![/red]")
return
self.console.print(Panel(f"当前用户信息:\n"
f"用户名:{user_info.pw_name}\n"
f"UID:{user_info.pw_uid}\n"
f"GID:{user_info.pw_gid}\n"
f"主目录:{user_info.pw_dir}\n"
f"Shell:{user_info.pw_shell}"))
new_home = Prompt.ask("请输入新的主目录", default=user_info.pw_dir)
new_shell = Prompt.ask("请输入新的shell", default=user_info.pw_shell)
cmd = ["usermod", "-d", new_home, "-s", new_shell, username]
success, output = self.run_command(cmd)
if success:
self.console.print(f"[green]成功修改用户 {username} 的信息[/green]")
else:
self.console.print(f"[red]修改用户信息失败:{output}[/red]")
except KeyboardInterrupt:
self.console.print("\n[yellow]已取消修改用户信息[/yellow]")
def list_groups(self):
"""列出所有用户组"""
table = Table(title="系统用户组列表")
table.add_column("组名", style="cyan")
table.add_column("GID", style="green")
table.add_column("成员", style="yellow")
for group in grp.getgrall():
members = ", ".join(group.gr_mem) if group.gr_mem else "无"
table.add_row(
group.gr_name,
str(group.gr_gid),
members
)
self.console.print(table)
def create_group(self):
"""创建新用户组"""
groupname = Prompt.ask("请输入新组名")
# 检查组是否已存在
try:
grp.getgrnam(groupname)
self.console.print(f"[red]错误:组 {groupname} 已存在![/red]")
return
except KeyError:
pass
cmd = ["groupadd", groupname]
success, output = self.run_command(cmd)
if success:
self.console.print(f"[green]成功创建组 {groupname}[/green]")
else:
self.console.print(f"[red]创建组失败:{output}[/red]")
def delete_group(self):
"""删除用户组"""
groupname = Prompt.ask("请输入要删除的组名")
# 检查组是否存在
try:
grp.getgrnam(groupname)
except KeyError:
self.console.print(f"[red]错误:组 {groupname} 不存在![/red]")
return
cmd = ["groupdel", groupname]
success, output = self.run_command(cmd)
if success:
self.console.print(f"[green]成功删除组 {groupname}[/green]")
else:
self.console.print(f"[red]删除组失败:{output}[/red]")
def add_user_to_group(self):
"""将用户添加到组"""
username = Prompt.ask("请输入用户名")
groupname = Prompt.ask("请输入组名")
# 检查用户和组是否存在
try:
pwd.getpwnam(username)
except KeyError:
self.console.print(f"[red]错误:用户 {username} 不存在![/red]")
return
try:
grp.getgrnam(groupname)
except KeyError:
self.console.print(f"[red]错误:组 {groupname} 不存在![/red]")
return
cmd = ["usermod", "-a", "-G", groupname, username]
success, output = self.run_command(cmd)
if success:
self.console.print(f"[green]成功将用户 {username} 添加到组 {groupname}[/green]")
else:
self.console.print(f"[red]添加用户到组失败:{output}[/red]")
def check_sudo_access(self, username: str) -> bool:
"""检查用户是否有sudo权限"""
try:
# 检查sudoers文件
cmd = f"grep -E '^{username}|^%.*{username}' {self.sudoers_file}"
success, output = self.run_command(["bash", "-c", cmd])
if success and output.strip():
return True
# 检查sudoers.d目录下的文件
cmd = f"grep -r -E '^{username}|^%.*{username}' {self.sudoers_dir}"
success, output = self.run_command(["bash", "-c", cmd])
if success and output.strip():
return True
return False
except:
return False
def list_sudo_users(self):
"""列出所有具有sudo权限的用户"""
table = Table(title="Sudo权限用户列表")
table.add_column("用户名", style="cyan")
table.add_column("权限来源", style="green")
table.add_column("权限详情", style="yellow")
# 检查每个用户
for user in pwd.getpwall():
username = user.pw_name
if self.check_sudo_access(username):
# 查找权限来源
cmd = f"grep -r -E '^{username}|^%.*{username}' {self.sudoers_file} {self.sudoers_dir}"
success, output = self.run_command(["bash", "-c", cmd])
if success:
for line in output.strip().split('\n'):
if line:
source, *content = line.split(':', 1)
content = content[0] if content else "N/A"
source = source.replace(self.sudoers_file, "sudoers")
source = source.replace(self.sudoers_dir + '/', "sudoers.d/")
table.add_row(username, source, content.strip())
self.console.print(table)
def grant_sudo_access(self):
"""授予用户sudo权限"""
username = Prompt.ask("请输入要授予sudo权限的用户名")
try:
pwd.getpwnam(username)
except KeyError:
self.console.print(f"[red]错误:用户 {username} 不存在![/red]")
return
if self.check_sudo_access(username):
self.console.print(f"[yellow]用户 {username} 已经具有sudo权限[/yellow]")
return
# 创建新的sudoers文件
filename = f"{self.sudoers_dir}/{username}"
content = f"{username} ALL=(ALL) ALL"
try:
# 首先写入临时文件
temp_file = f"{filename}.tmp"
with open(temp_file, 'w') as f:
f.write(content + '\n')
# 检查语法
success, output = self.run_command(["visudo", "-c", "-f", temp_file])
if not success:
self.console.print(f"[red]错误:sudoers语法检查失败:{output}[/red]")
os.unlink(temp_file)
return
# 移动到最终位置
os.rename(temp_file, filename)
os.chmod(filename, 0o440)
self.console.print(f"[green]成功授予用户 {username} sudo权限[/green]")
except Exception as e:
self.console.print(f"[red]授予sudo权限失败:{str(e)}[/red]")
def revoke_sudo_access(self):
"""撤销用户的sudo权限"""
username = Prompt.ask("请输入要撤销sudo权限的用户名")
try:
pwd.getpwnam(username)
except KeyError:
self.console.print(f"[red]错误:用户 {username} 不存在![/red]")
return
if not self.check_sudo_access(username):
self.console.print(f"[yellow]用户 {username} 没有sudo权限[/yellow]")
return
# 查找并删除sudoers配置
filename = f"{self.sudoers_dir}/{username}"
if os.path.exists(filename):
try:
os.unlink(filename)
self.console.print(f"[green]成功撤销用户 {username} 的sudo权限[/green]")
except Exception as e:
self.console.print(f"[red]撤销sudo权限失败:{str(e)}[/red]")
else:
self.console.print(f"[yellow]警告:需要手动编辑 {self.sudoers_file} 来撤销权限[/yellow]")
def main_menu():
"""显示主菜单"""
manager = UserManager()
while True:
try:
console.clear()
console.print(Panel.fit(
"[bold cyan]Linux用户管理[/bold cyan]\n"
"1. 列出所有用户\n"
"2. 创建新用户\n"
"3. 删除用户\n"
"4. 修改用户信息\n"
"5. 设置用户密码\n"
"6. 列出所有用户组\n"
"7. 创建新用户组\n"
"8. 删除用户组\n"
"9. 将用户添加到组\n"
"10. 列出所有具有sudo权限的用户\n"
"11. 授予用户sudo权限\n"
"12. 撤销用户的sudo权限\n"
"0. 退出程序",
title="主菜单"
))
choice = Prompt.ask("请选择操作", choices=["0", "1", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6", "7", "8", "9", "10", "11", "12"])
if choice == "0":
console.print("[yellow]感谢使用,再见![/yellow]")
break
try:
if choice == "1":
manager.list_users()
elif choice == "2":
manager.create_user()
elif choice == "3":
manager.delete_user()
elif choice == "4":
manager.modify_user()
elif choice == "5":
manager.set_password()
elif choice == "6":
manager.list_groups()
elif choice == "7":
manager.create_group()
elif choice == "8":
manager.delete_group()
elif choice == "9":
manager.add_user_to_group()
elif choice == "10":
manager.list_sudo_users()
elif choice == "11":
manager.grant_sudo_access()
elif choice == "12":
manager.revoke_sudo_access()
Prompt.ask("\n按回车键继续...")
except KeyboardInterrupt:
console.print("\n[yellow]操作已取消[/yellow]")
try:
if Prompt.ask("\n是否返回主菜单?", choices=["y", "n"], default="y") == "n":
console.print("[yellow]感谢使用,再见![/yellow]")
return
except KeyboardInterrupt:
console.print("\n[yellow]感谢使用,再见![/yellow]")
return
except KeyboardInterrupt:
console.print("\n[yellow]感谢使用,再见![/yellow]")
break
if __name__ == "__main__":
try:
main_menu()
except Exception as e:
console.print(f"\n[red]发生错误:{str(e)}[/red]")
sys.exit(1)
vim requirements.txt
rich==12.6.0
click==8.0.4
##安装模块: pip3 install -r requirements.txt
9、 网络检测
1、网络输入输出总量监测
import psutil
def get_network_usage():
"""
获取并打印网络 I/O 模块的使用情况,包括发送和接收的字节数(单位:MB)。
"""
try:
# 获取网络 I/O 统计信息
net_io = psutil.net_io_counters()
# 计算发送和接收的字节数(转换为 MB)
bytes_received = net_io.bytes_recv / (2**20) # 转换为 MB
bytes_sent = net_io.bytes_sent / (2**20) # 转换为 MB
# 输出结果
print(f"总接收字节数: {bytes_received:.2f} MB")
print(f"总发送字节数: {bytes_sent:.2f} MB")
except Exception as e:
# 捕获异常并输出错误信息
print(f"获取网络 I/O 使用信息失败: {e}")
# 调用函数
get_network_usage()

10、远程控制主机,并执行命令
import paramiko
import sys
# 检查命令行参数是否正确
if len(sys.argv) < 5:
print("Usage: python ssh.py <hostname> <username> <password> <command1> [command2] [command3] ...")
sys.exit(1)
# 从命令行参数中提取主机信息和命令
hostname = sys.argv[1] # 主机 IP 地址
username = sys.argv[2] # 登录用户名
password = sys.argv[3] # 登录密码
commands = sys.argv[4:] # 命令列表,从第四个参数开始
# 创建 SSH 客户端对象
ssh = paramiko.SSHClient()
# 设置自动添加主机密钥策略
ssh.set_missing_host_key_policy(paramiko.AutoAddPolicy())
# 连接到远程主机
try:
ssh.connect(
hostname=hostname, # 主机 IP 地址
username=username, # 登录用户名
password=password # 登录密码
)
# 依次执行命令并打印输出
for idx, command in enumerate(commands):
print(f"\n------ 执行命令 '{command}' 的结果 ------")
try:
stdin, stdout, stderr = ssh.exec_command(command) # 执行命令并获取输出
# 打印标准输出
print(stdout.read().decode('utf-8'))
# 打印标准错误(如果存在)
error_output = stderr.read().decode('utf-8')
if error_output:
print(f"--- 错误输出 ---\n{error_output}")
# 显式关闭 stdin, stdout, stderr
stdin.close()
stdout.close()
stderr.close()
except Exception as e:
print(f"执行命令 '{command}' 时发生错误: {e}")
finally:
# 确保关闭 SSH 连接
ssh.close()
# 执行方法:
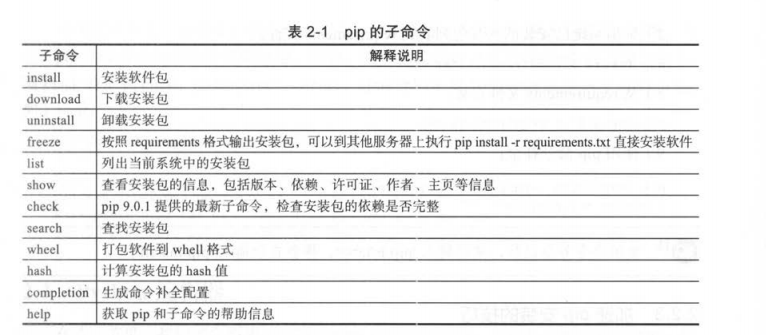
python3 ssh.py 192.168.1.100 root 1 'df -h' 'ip a s' 'ls -la'
11、服务监控,(状态,重启,关闭)
1、Nginx服务监控
import subprocess
def run_cmd(cmd):
try:
output = subprocess.run(["systemctl", "is-active", "nginx"], capture_output=True, text=True, check=True)
return output.stdout.strip() == "active"
except subprocess.CalledProcessError as e:
return False
def restart_nginx():
try:
subprocess.run(["systemctl", "restart", "nginx"], check=True)
print("Nginx restarted successfully")
return True
except subprocess.CalledProcessError as e:
print("Failed to restart Nginx")
print(e.stderr)
return False
if __name__ == "__main__":
if run_cmd("systemctl active nginx"):
print("Nginx is active")
else:
print("Nginx is not active")
if restart_nginx():
print("Nginx restarted successfully")
else:
print("Failed to restart Nginx")
12、CPU 监控
# 导入paramiko模块,用于SSH连接
import paramiko
# 导入time模块,用于处理时间
import time
# 导入smtplib模块,用于发送邮件
import smtplib
# 导入MIMEText类,用于创建邮件正文
from email.mime.text import MIMEText
# 导入MIMEMultipart库,用于创建邮件
from email.mime.multipart import MIMEMultipart
# 导入signal库,用于处理信号
import signal
# 定义一些常量
SSH_HOST = "192.168.1.100" # 监控的远程主机IP
SSH_PORT = 22 # SSH端口
SSH_USERNAME = "root" # SSH用户名
SSH_PASSWORD = "password123" # SSH密码
CPU_THRESHOLD = 80 # CPU使用率阈值(%)
# 邮件配置
SMTP_SERVER = "smtp.example.com" # SMTP服务器地址
SMTP_PORT = 587 # SMTP端口
SMTP_USERNAME = "sender@example.com" # SMTP用户名
SMTP_PASSWORD = "your_email_password" # SMTP密码
RECIPIENT_EMAIL = "admin@example.com" # 接收邮箱
# 信号处理函数,用于优雅退出
def graceful_exit(signal, frame):
print("\n接收到退出信号,程序优雅退出。")
client.close()
exit(0)
# 发送邮件通知
def send_email(cpu_usage, restarted_process):
message = MIMEText(
f"高CPU占用进程已被重启:{restarted_process}\n当前CPU使用率:{cpu_usage}%",
"plain",
"utf-8"
)
message["From"] = SMTP_USERNAME
message["To"] = RECIPIENT_EMAIL
message["Subject"] = "高CPU使用率警报"
try:
with smtplib.SMTP(SMTP_SERVER, SMTP_PORT) as server:
server.starttls() # 启用TLS加密
server.login(SMTP_USERNAME, SMTP_PASSWORD)
server.sendmail(SMTP_USERNAME, RECIPIENT_EMAIL, message.as_string())
print("已发送邮件通知。")
except Exception as e:
print(f"发送邮件失败:{e}")
# 主功能函数,监控CPU使用率并处理
def monitor_cpu_usage():
try:
# 创建SSH客户端
client = paramiko.SSHClient()
client.set_missing_host_key_policy(paramiko.AutoAddPolicy())
client.connect(SSH_HOST, port=SSH_PORT, username=SSH_USERNAME, password=SSH_PASSWORD)
while True:
# 执行命令获取CPU使用率
stdin, stdout, stderr = client.exec_command("mpstat 1 1 | grep all | awk '{print $12}'")
cpu_usage = float(stdout.read().decode().strip())
# 判断CPU使用率是否超过阈值
if cpu_usage > CPU_THRESHOLD:
print(f"高CPU警报:CPU使用率为 {cpu_usage}%(超过阈值 {CPU_THRESHOLD}%)")
# 执行重启操作(这里假设有一个重启命令)
stdin, stdout, stderr = client.exec_command("pkill -9 high_cpu_process && sleep 1 && /start_high_cpu_process.sh")
if stdout.channel.exit_status == 0:
print("进程已重启。")
# 发送邮件通知
send_email(cpu_usage, "high_cpu_process")
else:
print("重启失败。")
print(stderr.read().decode().strip())
else:
print(f"当前CPU使用率:{cpu_usage}%")
# 每5秒检查一次
time.sleep(5)
except paramiko.SSHException as e:
print(f"SSH连接失败:{e}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"发生错误:{e}")
finally:
client.close()
# 设置优雅退出的信号处理
signal.signal(signal.SIGINT, graceful_exit)
signal.signal(signal.SIGTERM, graceful_exit)
# 主程序入口
if __name__ == "__main__":
print("监控程序已启动,按 Ctrl+C 优雅退出。")
monitor_cpu_usage()
13、 使用进度条,查询任务执行速度
"""
from tqdm import tqdm
import time
try:
# 创建进度条实例
with tqdm(total=100, desc="山海摸鱼人正在工作") as pbar:
for i in range(10):
time.sleep(0.5) # 模拟耗时任务
pbar.update(10) # 每次更新10%
pbar.set_postfix({"状态": "努力摸鱼中"})
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("\n检测到用户中断,山海摸鱼人提前下班啦!")
finally:
print("清理工作完成")
"""
"""
• 使用with语句可以确保进度条正确关闭
• try-except捕获KeyboardInterrupt异常
• set_postfix用于显示额外状态信息
• finally块确保资源清理一定会执行
"""
from tqdm import tqdm
from multiprocessing import Pool, Manager
import time
def worker(task_id, queue):
"""模拟工作进程,通过 Queue 发送进度"""
for _ in range(10):
time.sleep(0.1 * (task_id + 1)) # 模拟耗时任务
queue.put(1) # 每次迭代发送一个信号
def run_parallel_tasks():
tasks = 5
total = tasks * 10
with tqdm(total=total, desc="协作进度") as pbar:
with Manager() as manager:
queue = manager.Queue() # 创建进程安全的队列
pool = Pool(tasks) # 创建进程池
result = pool.starmap_async(worker, [(i, queue) for i in range(tasks)]) # 异步启动所有任务
# 从队列中读取进度
for _ in range(total):
queue.get() # 阻塞直到收到一个信号
pbar.update(1)
# 确保所有子进程完成
result.wait()
if __name__ == '__main__':
run_parallel_tasks()
14、使用pyecharts进行图表制作
"""
from pyecharts.charts import Line
from pyecharts import options as opts
# 折线图
line = (
Line()
.add_xaxis(["周一", "周二", "周三", "周四", "周五", "周六", "周日"])
.add_yaxis("系列1", [120, 200, 150, 80, 70, 110, 130])
.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="折线图"))
)
line.render("line.html")
"""
""""
from pyecharts.charts import Bar
from pyecharts import options as opts
# 柱状图
bar = (
Bar()
.add_xaxis(["衬衫", "羊毛衫", "雪纺衫", "裤子", "高跟鞋", "袜子"])
.add_yaxis("商家A", [5, 20, 36, 10, 75, 90])
.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="柱状图"))
)
bar.render("line.html")
"""
"""
from pyecharts.charts import Scatter
from pyecharts import options as opts
# 散点图
scatter = (
Scatter()
.add_xaxis([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
.add_yaxis("series1", [10, 20, 30, 40, 50])
.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="散点图"))
)
scatter.render("line.html")
"""
"""
from pyecharts.charts import Pie
from pyecharts import options as opts
# 饼图
pie = (
Pie()
.add("", [list(z) for z in zip(["衬衫", "羊毛衫", "雪纺衫", "裤子", "高跟鞋", "袜子"], [5, 20, 36, 10, 75, 90])])
.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="饼图"))
.set_series_opts(label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(formatter="{b}: {c} ({d}%)"))
)
pie.render("pie.html")
"""
"""
from pyecharts.charts import Map
from pyecharts import options as opts
# 地图(以中国地图为例)
map_chart = (
Map()
.add("商家A", [list(z) for z in zip(['北京', '上海', '广东'], [55, 60, 70])], "china")
.set_global_opts(
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="地图"),
visualmap_opts=opts.VisualMapOpts(max_=200)
)
)
map_chart.render("map.html")
"""
""""
from pyecharts.charts import WordCloud
from pyecharts import options as opts
# 词云图
words = [
("Sam S Club", 10000),
("Macys", 6181),
("Amy Schumer", 4386),
]
wordcloud = (
WordCloud()
.add("", words, word_size_range=[20, 100], shape='circle')
.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="词云图"))
)
wordcloud.render("wordcloud.html")
"""
"""
from pyecharts.charts import Gauge
from pyecharts import options as opts
# 仪表盘
gauge = (
Gauge()
.add("", [("完成率", 88.99)])
.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="仪表盘"))
)
gauge.render("gauge.html")
"""
"""
from pyecharts.charts import Funnel
from pyecharts import options as opts
# 漏斗图
funnel = (
Funnel()
.add("商品", [list(z) for z in zip(["展现", "点击", "访问", "咨询", "订单"], [100, 80, 60, 40, 20])])
.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="漏斗图"))
)
funnel.render("funnel.html")
"""
""""
from pyecharts.charts import Tree, Parallel
from pyecharts import options as opts
# 树图
data = [
{
"name": "树节点",
"children": [
{"name": "子节点1"},
{"name": "子节点2", "children": [{"name": "孙子节点"}]}
]
}
]
tree = (
Tree()
.add("", data)
.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="树图"))
)
tree.render("tree.html")
# 平行坐标系图
parallel_data = [
['一部', 99, 92, 95, 95],
['二部', 99, 92, 95, 95],
]
parallel = (
Parallel()
.add_schema(
[
opts.ParallelAxisOpts(dim=0, name="部门"),
opts.ParallelAxisOpts(dim=1, name="综合素质", type_="value"),
opts.ParallelAxisOpts(dim=2, name="学科1", type_="value"),
opts.ParallelAxisOpts(dim=3, name="学科2", type_="value"),
opts.ParallelAxisOpts(dim=4, name="学科3", type_="value"),
]
)
.add("parallel", parallel_data)
.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="平行坐标系图"))
)
parallel.render("parallel.html")
"""
"""
from pyecharts.charts import Scatter3D
from pyecharts import options as opts
# 示例数据
data = [
[1, 1, 1],
[2, 2, 2],
[3, 3, 3],
[4, 4, 4],
[5, 5, 5]
]
scatter3d = (
Scatter3D()
.add("", data)
.set_global_opts(
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="3D 散点图"),
visualmap_opts=opts.VisualMapOpts(range_color=['#313695', '#4575b4', '#74add1', '#abd9e9', '#e0f3f8', '#ffffbf', '#fee090', '#fdae61', '#f46d43', '#d73027', '#a50026'])
)
)
scatter3d.render("scatter3d.html")
from pyecharts.charts import Bar, Timeline
from pyecharts import options as opts
# 时间线图
timeline = Timeline()
for i in range(2015, 2020):
bar = (
Bar()
.add_xaxis(["衬衫", "羊毛衫", "雪纺衫", "裤子", "高跟鞋", "袜子"])
.add_yaxis("商家A", [5 * i, 20 * i, 36 * i, 10 * i, 75 * i, 90 * i])
.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="{}年".format(i)))
)
timeline.add(bar, "{}年".format(i))
timeline.render("timeline.html")
from pyecharts.charts import Bar, Timeline
from pyecharts import options as opts
# 时间线图
timeline = Timeline()
for i in range(2015, 2020):
bar = (
Bar()
.add_xaxis(["衬衫", "羊毛衫", "雪纺衫", "裤子", "高跟鞋", "袜子"])
.add_yaxis("商家A", [5 * i, 20 * i, 36 * i, 10 * i, 75 * i, 90 * i])
.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="{}年".format(i)))
)
timeline.add(bar, "{}年".format(i))
timeline.render("timeline.html")
from pyecharts.charts import Bar, Timeline
from pyecharts import options as opts
# 时间线图
timeline = Timeline()
for i in range(2015, 2020):
bar = (
Bar()
.add_xaxis(["衬衫", "羊毛衫", "雪纺衫", "裤子", "高跟鞋", "袜子"])
.add_yaxis("商家A", [5 * i, 20 * i, 36 * i, 10 * i, 75 * i, 90 * i])
.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="{}年".format(i)))
)
timeline.add(bar, "{}年".format(i))
timeline.render("timeline.html")
from pyecharts.charts import Bar, Timeline
from pyecharts import options as opts
# 时间线图
timeline = Timeline()
for i in range(2015, 2020):
bar = (
Bar()
.add_xaxis(["衬衫", "羊毛衫", "雪纺衫", "裤子", "高跟鞋", "袜子"])
.add_yaxis("商家A", [5 * i, 20 * i, 36 * i, 10 * i, 75 * i, 90 * i])
.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="{}年".format(i)))
)
timeline.add(bar, "{}年".format(i))
timeline.render("timeline.html")
from pyecharts.charts import Bar, Timeline
from pyecharts import options as opts
# 时间线图
timeline = Timeline()
for i in range(2015, 2020):
bar = (
Bar()
.add_xaxis(["衬衫", "羊毛衫", "雪纺衫", "裤子", "高跟鞋", "袜子"])
.add_yaxis("商家A", [5 * i, 20 * i, 36 * i, 10 * i, 75 * i, 90 * i])
.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="{}年".format(i)))
)
timeline.add(bar, "{}年".format(i))
timeline.render("timeline.html")
from pyecharts.charts import Geo
from pyecharts import options as opts
# 地理坐标系图
geo = (
Geo()
.add_schema(maptype="china")
.add("geo", [("北京", 55), ("上海", 60), ("广州", 70)])
.set_series_opts(label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(is_show=False))
.set_global_opts(
visualmap_opts=opts.VisualMapOpts(),
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="地理坐标系图")
)
)
geo.render("geo.html")
### 平行坐标系图
from pyecharts.charts import Parallel
from pyecharts import options as opts
# 平行坐标系图
parallel_data = [
['一部', 99, 92, 95, 95],
['二部', 99, 92, 95, 95],
]
parallel = (
Parallel()
.add_schema(
[
opts.ParallelAxisOpts(dim=0, name="部门"),
opts.ParallelAxisOpts(dim=1, name="综合素质", type_="value"),
opts.ParallelAxisOpts(dim=2, name="学科1", type_="value"),
opts.ParallelAxisOpts(dim=3, name="学科2", type_="value"),
opts.ParallelAxisOpts(dim=4, name="学科3", type_="value"),
]
)
.add("parallel", parallel_data)
.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="平行坐标系图"))
)
parallel.render("parallel.html")
"""
"""
from pyecharts.charts import Surface3D
from pyecharts import options as opts
import numpy as np
x_data = y_data = list(range(-5, 5))
z_data = [[y, x, np.sin(np.sqrt(x ** 2 + y ** 2))] for x in x_data for y in y_data]
surface3d = (
Surface3D()
.add(
"",
z_data,
shading="color",
xaxis3d_opts=opts.Axis3DOpts(type_="value"),
yaxis3d_opts=opts.Axis3DOpts(type_="value"),
zaxis3d_opts=opts.Axis3DOpts(type_="value"),
)
.set_global_opts(
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="3D 曲面图(近似)"),
visualmap_opts=opts.VisualMapOpts(max_=1, min_=-1, range_color=['#313695', '#4575b4', '#74add1', '#abd9e9', '#e0f3f8', '#ffffbf', '#fee090', '#fdae61', '#f46d43', '#d73027', '#a50026'])
)
)
surface3d.render("surface3d.html")
"""
"""
from pyecharts.charts import Surface3D
from pyecharts import options as opts
import numpy as np
x_data = y_data = list(range(-5, 5))
z_data = [[y, x, np.sin(np.sqrt(x ** 2 + y ** 2))] for x in x_data for y in y_data]
surface3d = (
Surface3D()
.add(
"",
z_data,
shading="color",
xaxis3d_opts=opts.Axis3DOpts(type_="value"),
yaxis3d_opts=opts.Axis3DOpts(type_="value"),
zaxis3d_opts=opts.Axis3DOpts(type_="value"),
)
.set_global_opts(
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="3D 曲面图(近似)"),
visualmap_opts=opts.VisualMapOpts(max_=1, min_=-1, range_color=['#313695', '#4575b4', '#74add1', '#abd9e9', '#e0f3f8', '#ffffbf', '#fee090', '#fdae61', '#f46d43', '#d73027', '#a50026'])
)
)
surface3d.render("surface3d.html")
"""
"""
from pyecharts.charts import Surface3D
from pyecharts import options as opts
import numpy as np
x_data = y_data = list(range(-5, 5))
z_data = [[y, x, np.sin(np.sqrt(x ** 2 + y ** 2))] for x in x_data for y in y_data]
surface3d = (
Surface3D()
.add(
"",
z_data,
shading="color",
xaxis3d_opts=opts.Axis3DOpts(type_="value"),
yaxis3d_opts=opts.Axis3DOpts(type_="value"),
zaxis3d_opts=opts.Axis3DOpts(type_="value"),
)
.set_global_opts(
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="3D 曲面图(近似)"),
visualmap_opts=opts.VisualMapOpts(max_=1, min_=-1, range_color=['#313695', '#4575b4', '#74add1', '#abd9e9', '#e0f3f8', '#ffffbf', '#fee090', '#fdae61', '#f46d43', '#d73027', '#a50026'])
)
)
surface3d.render("surface3d.html")
"""
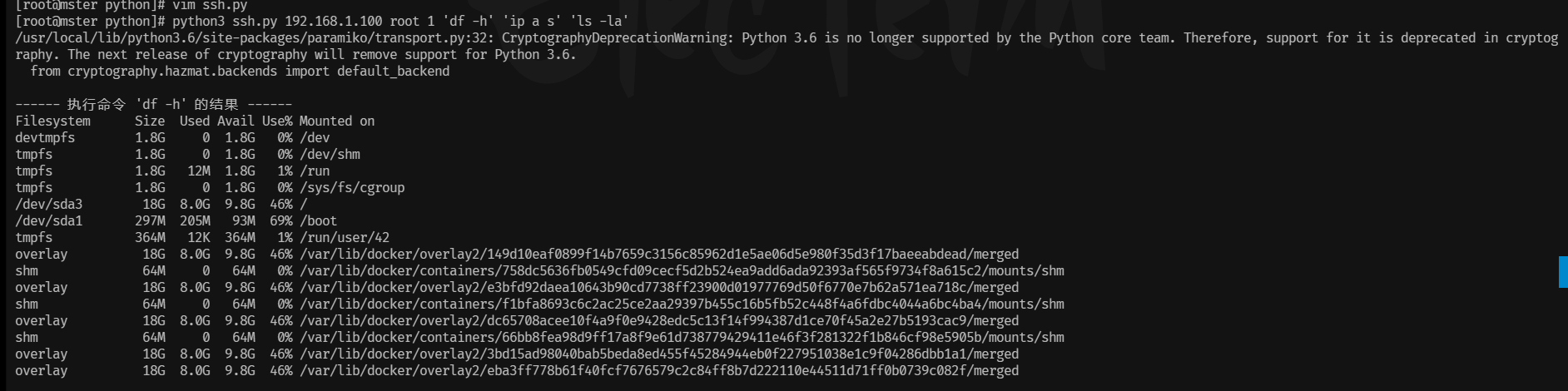
15、使用click库做数据库监控
import click
import mysql.connector
from mysql.connector import Error
import shutil
# 数据库配置(可通过命令行参数覆盖)
DEFAULT_CONFIG = {
"host": "127.0.0.1",
"user": "root",
"password": "Suking@987#",
"port": 3306,
"database": "mysql"
}
@click.group()
def cli():
"""MySQL 数据库监控工具"""
pass
@cli.command()
@click.option('--max-conn', default=100, help='最大允许连接数阈值,默认100')
def check_connections(max_conn):
"""监控当前数据库连接数"""
try:
conn = mysql.connector.connect(**DEFAULT_CONFIG)
cursor = conn.cursor()
cursor.execute("SHOW GLOBAL STATUS LIKE 'Threads_connected'")
current_conn = cursor.fetchone()[1]
click.secho(f"当前连接数: {current_conn}", fg='green')
if int(current_conn) > max_conn:
click.secho(f"⚠️ 警告:连接数超过阈值 ({max_conn})!", fg='red', blink=True)
raise click.Abort()
except Error as e:
click.secho(f"数据库连接失败: {e}", fg='red')
raise click.Abort()
finally:
if conn.is_connected():
cursor.close()
conn.close()
@cli.command()
@click.option('--slow-threshold', default=1, help='慢查询阈值(秒),默认1秒')
def check_slow_queries(slow_threshold):
"""监控慢查询数量"""
try:
conn = mysql.connector.connect(**DEFAULT_CONFIG)
cursor = conn.cursor()
cursor.execute("SHOW GLOBAL STATUS LIKE 'Slow_queries'")
slow_queries = cursor.fetchone()[1]
click.secho(f"累计慢查询次数: {slow_queries}", fg='yellow')
if int(slow_queries) > 0:
click.secho(f"⚠️ 存在慢查询(阈值={slow_threshold}s)", fg='red')
except Error as e:
click.secho(f"数据库连接失败: {e}", fg='red')
raise click.Abort()
finally:
if conn.is_connected():
cursor.close()
conn.close()
@cli.command()
@click.option('--disk-threshold', default=90, help='磁盘使用率阈值(百分比),默认90%')
def check_disk_usage(disk_threshold):
"""监控数据库存储目录磁盘空间"""
total, used, free = shutil.disk_usage("/var/lib/mysql")
usage_percent = (used / total) * 100
click.secho(f"磁盘使用率: {usage_percent:.1f}%", fg='blue')
if usage_percent > disk_threshold:
click.secho(f"⚠️ 磁盘空间不足(超过{disk_threshold}%)", fg='red')
raise click.Abort()
if __name__ == '__main__':
cli()
16、json文件检查
import json
# 读取文件内容
with open('conn.json', 'r') as file:
content = file.read()
print("读取的内容:")
print(content)
# 尝试解析 JSON
try:
conf = json.loads(content)
print("解析成功:")
print(conf)
except json.JSONDecodeError as e:
print("JSON 解析错误:")
print(e)
17 、yaml 语法检查
import yaml
def validate_yaml_syntax(file_path):
"""验证 YAML 语法有效性"""
try:
with open(file_path, 'r') as f:
yaml.safe_load(f)
return True
except yaml.YAMLError as e:
print(f"语法错误: {e.problem} (行号: {e.problem_mark.line+1})") # 精准定位错误[7](@ref)
return False
except FileNotFoundError:
print(f"错误: 文件 {file_path} 不存在")
return False
def validate_k8s_pod(file_path):
"""验证 Kubernetes Pod 结构"""
try:
with open(file_path, 'r') as f:
data = yaml.safe_load(f)
required = ['apiVersion', 'kind', 'metadata', 'spec']
for field in required:
if field not in data:
print(f"关键字段缺失: {field}")
return False
if data['kind'].lower() != 'pod':
print("Kind 必须是 Pod")
return False
containers = data['spec'].get('containers', [])
if not containers:
print("必须定义至少一个容器")
return False
for idx, container in enumerate(containers):
if 'name' not in container:
print(f"容器 {idx} 缺少 name 字段")
return False
if 'image' not in container:
print(f"容器 {container.get('name')} 缺少 image 字段")
return False
print("Pod 结构验证通过")
return True
except Exception as e:
print(f"验证异常: {str(e)}")
return False
# 示例调用
if __name__ == "__main__":
yaml_file = "/root/yaml/pod.yaml"
if validate_yaml_syntax(yaml_file):
validate_k8s_pod(yaml_file)
18、 使用click 执行远程主机命令
import click
import paramiko
from paramiko import SSHClient, AutoAddPolicy
@click.group()
def cli():
"""远程服务器管理工具"""
pass
@cli.command()
@click.option('--host', required=True, help='远程服务器IP')
@click.option('--port', default=22, help='SSH端口,默认22')
@click.option('--user', default='root', help='用户名,默认root')
@click.option('--password', prompt=True, hide_input=True, help='SSH密码')
@click.option('--command', required=True, help='要执行的远程命令')
def exec_remote(host, port, user, password, command):
"""通过SSH执行远程命令"""
client = SSHClient()
client.set_missing_host_key_policy(AutoAddPolicy())
try:
# 连接服务器
client.connect(host, port=port, username=user, password=password)
# 执行命令
stdin, stdout, stderr = client.exec_command(command)
exit_code = stdout.channel.recv_exit_status()
# 输出结果
click.secho(f"Exit Code: {exit_code}", fg='blue')
if stdout:
click.echo("标准输出:")
click.secho(stdout.read().decode(), fg='green')
if stderr:
click.echo("错误输出:")
click.secho(stderr.read().decode(), fg='red')
except Exception as e:
click.secho(f"连接或执行失败: {str(e)}", fg='red', bold=True)
finally:
client.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
cli()
19、 click库执行多个IP多个命令
import click
import paramiko
from paramiko import SSHClient, AutoAddPolicy
from time import sleep
# 全局配置(超时时间、命令间隔)
CONFIG = {"timeout": 10, "cmd_interval": 0.5}
@click.group()
def cli():
"""远程服务器批量管理工具"""
pass
def execute_commands(host, port, user, password, commands):
"""单台服务器执行多命令的核心逻辑"""
client = SSHClient()
client.set_missing_host_key_policy(AutoAddPolicy())
try:
client.connect(host, port=port, username=user, password=password, timeout=CONFIG["timeout"])
click.secho(f"\n🔗 连接成功:{user}@{host}:{port}", fg="cyan", bold=True)
# 按顺序执行所有命令
for idx, cmd in enumerate(commands, 1):
click.echo(f"\n🚀 执行命令 [{idx}/{len(commands)}]: {click.style(cmd, fg='yellow')}")
stdin, stdout, stderr = client.exec_command(cmd)
exit_code = stdout.channel.recv_exit_status()
# 输出结果解析
click.secho(f"Exit Code: {exit_code}", fg="blue")
if stdout:
click.echo("标准输出:")
click.secho(stdout.read().decode().strip(), fg="green")
if stderr:
click.echo("错误输出:")
click.secho(stderr.read().decode().strip(), fg="red")
sleep(CONFIG["cmd_interval"]) # 避免命令执行过快
except Exception as e:
click.secho(f"❌ 连接或执行失败:{str(e)}", fg="red", bold=True)
finally:
client.close()
click.echo("━" * 50)
@cli.command()
@click.option('--hosts', required=True, help='远程服务器IP列表(逗号分隔)')
@click.option('--port', default=22, help='SSH端口,默认22')
@click.option('--user', default='root', help='用户名,默认root')
@click.option('--password', prompt=True, hide_input=True, help='SSH密码')
@click.option('--commands', required=True, help='要执行的命令列表(分号分隔)')
def batch_exec(hosts, port, user, password, commands):
"""批量执行多IP多命令"""
host_list = [h.strip() for h in hosts.split(",") if h.strip()]
cmd_list = [c.strip() for c in commands.split(";") if c.strip()]
if not host_list or not cmd_list:
click.secho("❌ 输入参数无效:IP或命令列表为空", fg="red")
return
click.secho(f"📡 开始批量任务 | 主机数:{len(host_list)} | 命令数:{len(cmd_list)}", fg="magenta", bold=True)
# 按顺序执行每个主机的所有命令
for host in host_list:
execute_commands(host, port, user, password, cmd_list)
if __name__ == '__main__':
cli()
"""
命令执行方法:
# 监控三台主机的磁盘和进程
python batch_ssh.py batch-exec \
--hosts "192.168.1.100,10.0.0.5,172.16.8.20" \
--user admin \
--password "your_password" \
--commands "df -h;free -m;ps aux"
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献3条内容
已为社区贡献3条内容







所有评论(0)