bert使用做文本分类
Most of the researchers submit their research papers to academic conference because its a faster way of making the results available. Finding and selecting a suitable conference has always been challenging especially for young researchers.
大多数研究人员将其研究论文提交学术会议,因为这是一种更快获得结果的方法。 寻找和选择合适的会议一直是挑战,尤其是对于年轻的研究人员而言。
However, based on the previous conferences proceeding data, the researchers can increase their chances of paper acceptance and publication. We will try to solve this text classification problem with deep learning using BERT.
但是,根据以前的会议进行的数据,研究人员可以增加论文被接受和发表的机会。 我们将尝试通过使用BERT进行深度学习来解决此文本分类问题。
Almost all the code were taken from this tutorial, the only difference is the data.
几乎所有代码都来自本教程 ,唯一的区别是数据。
数据 (The Data)
The dataset contains 2,507 research paper titles, and have been manually classified into 5 categories (i.e. conferences) that can be downloaded from here.
该数据集包含2,507个研究论文标题,并且已被手动分为5类(即会议),可以从此处下载。
探索和预处理 (Explore and Preprocess)
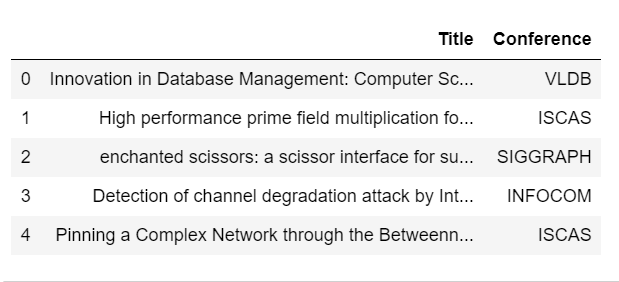
df['Conference'].value_counts()
You may have noticed that our classes are imbalanced, and we will address this later on.
您可能已经注意到我们的班级不平衡,我们将在稍后解决。
编码标签 (Encoding the Labels)
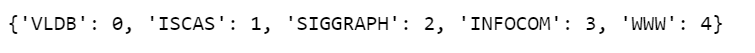
df['label'] = df.Conference.replace(label_dict)训练和验证拆分 (Train and Validation Split)
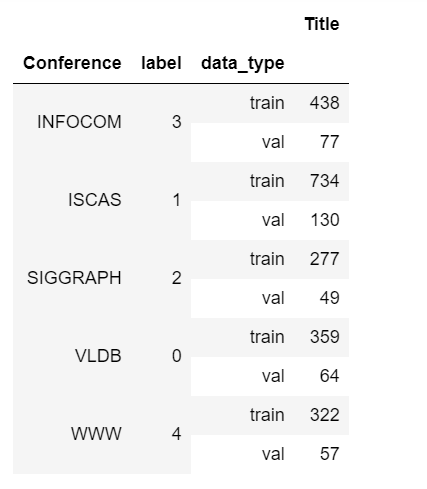
Because the labels are imbalanced, we split the data set in a stratified fashion, using this as the class labels.
由于标签不平衡,因此我们将数据集分层使用此标签作为类标签。
Our labels distribution will look like this after the split.
拆分后,我们的标签分布将如下所示。
BertTokenizer和数据编码 (BertTokenizer and Encoding the Data)
Tokenization is a process to take raw texts and split into tokens, which are numeric data to represent words.
令牌化是获取原始文本并将其拆分为令牌的过程,令牌是表示单词的数字数据。
-
Constructs a BERT tokenizer. Based on WordPiece.
构造一个BERT令牌生成器 。 基于WordPiece。
- Instantiate a pre-trained BERT model configuration to encode our data. 实例化预训练的BERT模型配置以对我们的数据进行编码。
-
To convert all the titles from text into encoded form, we use a function called
batch_encode_plus, and we will proceed train and validation data separately.要将所有标题从文本转换为编码形式,我们使用一个名为
batch_encode_plus的函数,我们将分别进行训练和验证数据。 - The 1st parameter inside the above function is the title text. 上面函数中的第一个参数是标题文本。
-
add_special_tokens=Truemeans the sequences will be encoded with the special tokens relative to their model.add_special_tokens=True表示序列将使用相对于其模型的特殊标记进行编码。 -
When batching sequences together, we set
return_attention_mask=True, so it will return the attention mask according to the specific tokenizer defined by themax_lengthattribute.将序列分批处理时,我们设置
return_attention_mask=True,因此它将根据max_length属性定义的特定标记生成器返回注意掩码。 - We also want to pad all the titles to certain maximum length. 我们还希望将所有标题填充到一定的最大长度。
-
We actually do not need to set
max_length=256, but just to play it safe.实际上,我们不需要设置
max_length=256,而是为了安全起见。 -
return_tensors='pt'to return PyTorch.return_tensors='pt'返回PyTorch。 -
And then we need to split the data into
input_ids,attention_masksandlabels.然后,我们需要将数据拆分为
input_ids,attention_masks和labels。 - Finally, after we get encoded data set, we can create training data and validation data. 最后,在获得编码数据集之后,我们可以创建训练数据和验证数据。
BERT预训练模型 (BERT Pre-trained Model)
We are treating each title as its unique sequence, so one sequence will be classified to one of the five labels (i.e. conferences).
我们将每个标题视为其唯一序列,因此一个序列将被分类为五个标签(即会议)之一。
-
bert-base-uncasedis a smaller pre-trained model.bert-base-uncased是一个较小的预训练模型。 -
Using
num_labelsto indicate the number of output labels.使用
num_labels指示输出标签的数量。 -
We don’t really care about
output_attentions.我们并不在乎
output_attentions。 -
We also don’t need
output_hidden_states.我们也不需要
output_hidden_states。
数据加载器 (Data Loaders)
-
DataLoadercombines a dataset and a sampler, and provides an iterable over the given dataset.DataLoader结合了数据集和采样器,并在给定的数据集上提供了可迭代的功能。 -
We use
RandomSamplerfor training andSequentialSamplerfor validation.我们使用
RandomSampler进行训练,使用SequentialSampler进行验证。 -
Given the limited memory in my environment, I set
batch_size=3.考虑到我的环境中有限的内存,我设置
batch_size=3。
优化器和调度器 (Optimizer & Scheduler)
- To construct an optimizer, we have to give it an iterable containing the parameters to optimize. Then, we can specify optimizer-specific options such as the learning rate, epsilon, etc. 要构建优化器,我们必须给它一个包含可优化参数的可迭代器。 然后,我们可以指定特定于优化程序的选项,例如学习率,ε等。
-
I found
epochs=5works well for this data set.我发现
epochs=5对于此数据集效果很好。 - Create a schedule with a learning rate that decreases linearly from the initial learning rate set in the optimizer to 0, after a warmup period during which it increases linearly from 0 to the initial learning rate set in the optimizer. 在预热阶段之后,创建一个计划,使其学习率从优化器中设置的初始学习率线性降低到0,在此期间,学习率从0线性增加到优化器中设置的初始学习率。
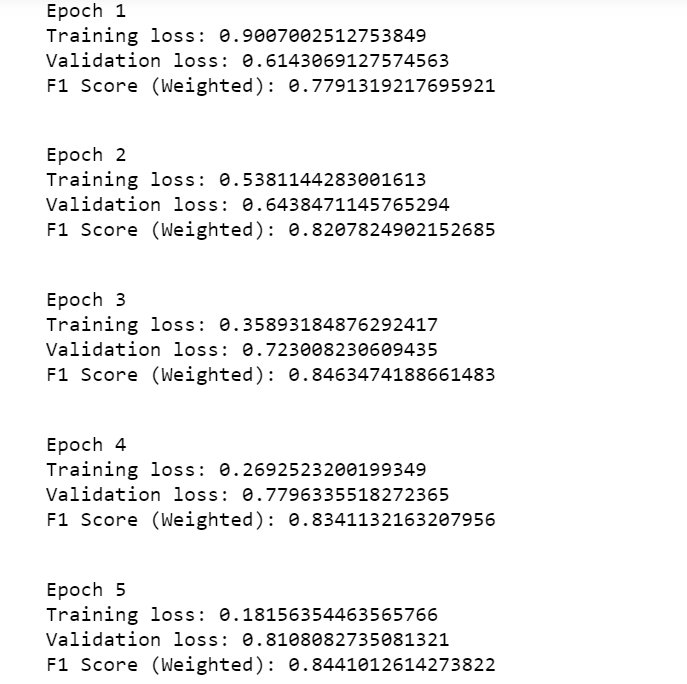
性能指标 (Performance Metrics)
We will use f1 score and accuracy per class as performance metrics.
我们将使用f1分数和每个班级的准确性作为绩效指标。
训练循环 (Training Loop)
加载和评估模型 (Loading and Evaluating the Model)

Jupyter notebook can be found on Github. Enjoy the rest of the weekend!
Jupyter笔记本可以在Github上找到。 周末愉快!
bert使用做文本分类








 已为社区贡献8条内容
已为社区贡献8条内容

所有评论(0)