吴恩达深度学习课程-Course 4 卷积神经网络 第一周 卷积神经网络编程作业(第二部分)
这个版本有点问题...1.1和1.2是基于tf2框架改的兼容tf1的版本,1.3和1.4没改,尝试改过报一堆错。。。多学习学习再看看好了
【注意】!!!!这个代码基于tf1,但是笔者装的tf2框架,实在改不动了,1.1和1.2还能勉强跑通,1.3怎么改都报错,所以1.3放的是原始tf1的代码
卷积神经网络: 应用
欢迎来到课程4的第二份作业!在这此次作业里,你可以:
- 实现在实现TensorFlow模型时使用的帮助函数
- 使用TensorFlow实现一个功能完整的ConvNet
完成这个任务后,你将能够:
- 在TensorFlow中构建和训练一个卷积神经网络来解决一个分类问题
我们假设你已经熟悉TensorFlow。如果你还没有,请参考课程2第三周的TensorFlow教程(“改进深度神经网络”)。
1.0 - TensorFlow模型
在之前的作业中,您使用numpy构建了帮助函数,以理解卷积神经网络背后的机制。目前大多数实际的深度学习应用程序都是使用编程框架构建的,这些框架有许多可以简单调用的内置函数。
和往常一样,我们将从导入库开始。
import math
import numpy as np
import h5py
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import scipy
from PIL import Image
from scipy import ndimage
#import tensorflow as tf
"""
注意我用的是tf2,如果想禁掉tf2,只用tf1的功能就这么写
但是我这次写作业的时候,不知道为啥这样写,用jupyter禁不掉tf2,用pycharm可,麻了....
所以我后面的代码都会加tf.compat.v1,如果能禁成功,直接tf.就行
"""
import tensorflow.compat.v1 as tf
tf.disable_v2_behavior()
from tensorflow.python.framework import ops
from cnn_utils import *
%matplotlib inline
np.random.seed(1)
【注意】:如果显示没有scipy,在anaconda prompt里面输入conda install scipy即可,名字输错了找了半天错,麻了…
运行下一个单元格来加载将要使用的“SIGNS”数据集。
# Loading the data (signs)
X_train_orig, Y_train_orig, X_test_orig, Y_test_orig, classes = load_dataset()
提醒一下,SIGNS数据集是6个符号的集合,表示从0到5的数字。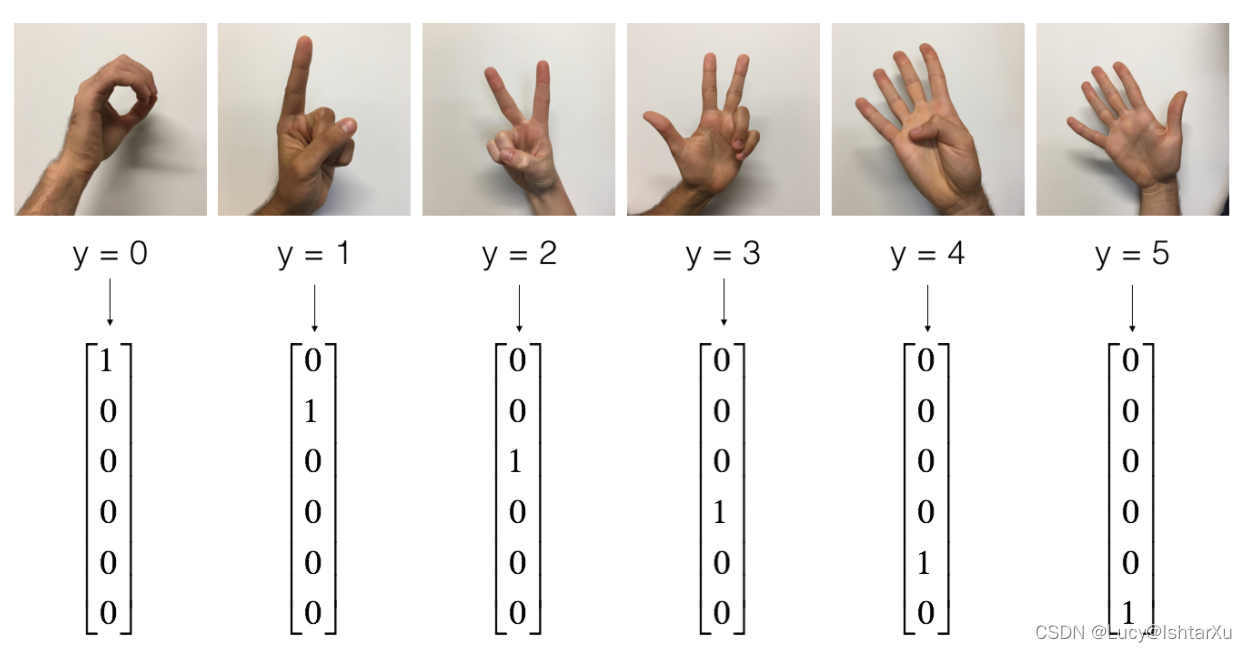
下一个单元格将向您展示数据集中带有标签的图像的示例。请随意更改下面index的值,并重新运行以查看不同的示例。
# Example of a picture
index = 6
plt.imshow(X_train_orig[index])
print ("y = " + str(np.squeeze(Y_train_orig[:, index])))
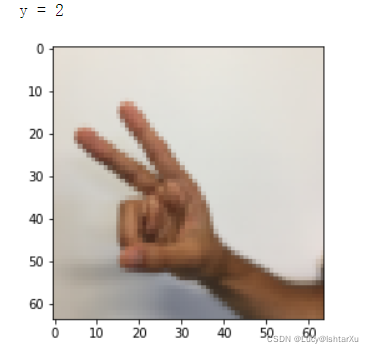
在课程2中,您已经为这个数据集构建了一个全连接网络。但由于这是一个图像数据集,因此更自然的做法是将ConvNet应用于它。
首先,让我们检查一下数据的形状。
X_train = X_train_orig/255.
X_test = X_test_orig/255.
Y_train = convert_to_one_hot(Y_train_orig, 6).T
Y_test = convert_to_one_hot(Y_test_orig, 6).T
print ("number of training examples = " + str(X_train.shape[0]))
print ("number of test examples = " + str(X_test.shape[0]))
print ("X_train shape: " + str(X_train.shape))
print ("Y_train shape: " + str(Y_train.shape))
print ("X_test shape: " + str(X_test.shape))
print ("Y_test shape: " + str(Y_test.shape))
conv_layers = {}
输出结果为
number of training examples = 1080
number of test examples = 120
X_train shape: (1080, 64, 64, 3)
Y_train shape: (1080, 6)
X_test shape: (120, 64, 64, 3)
Y_test shape: (120, 6
1.1 - 创建占位符
TensorFlow要求您为将在运行会话时输入到模型中的输入数据创建占位符。
【练习】:实现下面的函数,为输入图像 X X X和输出图像 Y Y Y创建占位符。目前不应该定义训练示例的数量。为此,您可以使用“None”作为批处理大小,它将为您提供以后选择它的灵活性。因此X的维度应该是[None, n_H0, n_W0, n_C0], Y的维度应该是[None, n_y]。提示
# GRADED FUNCTION: create_placeholders
def create_placeholders(n_H0, n_W0, n_C0, n_y):
"""
Creates the placeholders for the tensorflow session.
Arguments:
n_H0 -- scalar, height of an input image
n_W0 -- scalar, width of an input image
n_C0 -- scalar, number of channels of the input
n_y -- scalar, number of classes
Returns:
X -- placeholder for the data input, of shape [None, n_H0, n_W0, n_C0] and dtype "float"
Y -- placeholder for the input labels, of shape [None, n_y] and dtype "float"
"""
### START CODE HERE ### (≈2 lines)
"""
如果这里是tf1的,直接写
X = tf.placeholder(shape=[None, n_H0, n_W0, n_C0], dtype = "float")
Y = tf.placeholder(shape=[None, n_y], dtype = "float")
"""
X = tf.compat.v1.placeholder(shape=[None, n_H0, n_W0, n_C0], dtype = "float")
Y = tf.compat.v1.placeholder(shape=[None, n_y], dtype = "float")
### END CODE HERE ###
return X, Y
X, Y = create_placeholders(64, 64, 3, 6)
print ("X = " + str(X))
print ("Y = " + str(Y))
输出结果为
X = Tensor("Placeholder:0", shape=(?, 64, 64, 3), dtype=float32)
Y = Tensor("Placeholder_1:0", shape=(?, 6), dtype=float32)
1.2 - 初始化参数
你将使用tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer(seed = 0)初始化weights/filter 𝑊 1 𝑊1 W1和 𝑊 2 𝑊2 W2。你不需要担心偏差变量,因为你很快就会看到TensorFlow函数处理偏差。还请注意,您将只初始化conv2d函数的权重/过滤器。TensorFlow自动初始化全连接部分的层。我们在以后的作业中会详细讨论。
【注意】:tf2把上面那个函数取消了,经测试,tf.initializers.GlorotUniform()和上面函数效果一致
练习:实现initialize_parameters()。下面提供了每组过滤器的尺寸。提示:初始化Tensorflow中shape[1,2,3,4]的参数 𝑊 𝑊 W,使用:
W = tf.get_variable("W", [1,2,3,4], initializer = ...)
# GRADED FUNCTION: initialize_parameters
def initialize_parameters():
"""
Initializes weight parameters to build a neural network with tensorflow. The shapes are:
W1 : [4, 4, 3, 8]
W2 : [2, 2, 8, 16]
Returns:
parameters -- a dictionary of tensors containing W1, W2
如果可以把tf2禁了,不需要我这么麻烦
"""
tf.compat.v1.set_random_seed(1) # so that your "random" numbers match ours
### START CODE HERE ### (approx. 2 lines of code)
W1 = tf.compat.v1.get_variable("W1",[4, 4, 3, 8], initializer = tf.initializers.GlorotUniform())
W2 = tf.compat.v1.get_variable("W2",[2, 2, 8, 16], initializer =tf.initializers.GlorotUniform())
### END CODE HERE ###
parameters = {"W1": W1,
"W2": W2}
return parameters
tf.compat.v1.reset_default_graph()
with tf.compat.v1.Session() as sess_test:
parameters = initialize_parameters()
init = tf.compat.v1.global_variables_initializer()
sess_test.run(init)
print("W1 = " + str(parameters["W1"].eval()[1,1,1]))
print("W2 = " + str(parameters["W2"].eval()[1,1,1]))
输出结果
和官方不一样…找到错误再说吧
W1 = [ 0.00131723 0.1417614 -0.04434952 0.09197326 0.14984085 -0.03514394
-0.06847463 0.05245192]
W2 = [ 0.19037306 0.05684656 0.1125446 -0.23109215 -0.22926426 0.04337913
-0.12032002 -0.01428771 0.04773349 0.1976018 0.0700236 0.24014717
-0.2141701 0.09505171 -0.19955802 0.19850826]
1.3 - 前向传播
在TensorFlow中,有一些内置函数可以帮你完成卷积的步骤。
tf.nn.conv2d(X,W1, strides = [1,s,s,1], padding = 'SAME'):给定一个输入 𝑋 𝑋 X和一组过滤器𝑊1,该函数对𝑊1的过滤器 X X X进行卷积。第三个输入([1,f,f,1])表示输入(m, n_H_prev, n_W_prev, n_C_prev)的每个维度的strides。你可以在这里阅读完整的文档tf.nn.max_pool(A, ksize = [1,f,f,1], strides = [1,s,s,1], padding = 'SAME'):给定一个输入A,这个函数使用一个大小为(f, f)的窗口和大小为(s, s)的strides来对每个窗口执行max pooling。你可以在这里阅读完整的文档tf.nn.relu(Z1):计算Z1的elementwise ReLU(可以是任何形状)。你可以在这里阅读完整的文档。tf.contrib.layers.flatten(P):给定一个输入P,该函数将每个样本扁平化为一个1D向量,同时保持批处理大小。它返回一个扁平的张量,形状为[batch_size, k]。你可以在这里阅读完整的文档。tf.contrib.layers.fully_connected(F, num_outputs):
给定一个扁平的输入F,它返回使用全连接层计算得到的输出。你可以在这里阅读完整的文档。
在上面的最后一个函数tf.contrib.layers.fully_connected(F, num_outputs):中,全连接层自动初始化图中的权值,并在训练模型时继续训练它们。因此,在初始化参数时,不需要初始化这些权重。
练习:
实现下面的forward_propagation函数,构建如下模型:CONV2D -> RELU -> MAXPOOL -> CONV2D -> RELU -> MAXPOOL -> FLATTEN -> fullconnected。您应该使用上面的函数。
在细节中,我们将使用以下参数的所有步骤:
Conv2D:步长=1,填充“SAME”
ReLU - Max pool:使用一个8x8过滤器的大小和一个8×8步长,填充“SAME”Conv2D:步长=1,填充“SAME”
ReLU
Max pooling:使用一个4×4过滤器的大小和一个4×4步长,填充“SAME”
展平之前的输出
FC (full - connected)层:全连接层,无非线性激活功能。
不要在这里调用softmax。这将导致输出层中有6个神经元,然后这些神经元随后被传递到softmax。在TensorFlow中,softmax和cost函数被合并到一个单独的函数中,当计算cost时,你会调用一个不同的函数。
# GRADED FUNCTION: forward_propagation
def forward_propagation(X, parameters):
"""
Implements the forward propagation for the model:
CONV2D -> RELU -> MAXPOOL -> CONV2D -> RELU -> MAXPOOL -> FLATTEN -> FULLYCONNECTED
Arguments:
X -- input dataset placeholder, of shape (input size, number of examples)
parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters "W1", "W2"
the shapes are given in initialize_parameters
Returns:
Z3 -- the output of the last LINEAR unit
以下都是tf1的代码,不改了。。。我用tf2疯狂报错,改不动了- -
"""
# Retrieve the parameters from the dictionary "parameters"
W1 = parameters['W1']
W2 = parameters['W2']
### START CODE HERE ###
# CONV2D: stride of 1, padding 'SAME'
Z1 = tf.nn.conv2d(X,W1, strides = [1,1,1,1], padding = 'SAME')
# RELU
A1 = tf.nn.relu(Z1)
# MAXPOOL: window 8x8, sride 8, padding 'SAME'
P1 = tf.nn.max_pool(A1, ksize = [1,8,8,1], strides = [1,8,8,1], padding = 'SAME')
# CONV2D: filters W2, stride 1, padding 'SAME'
Z2 = tf.nn.conv2d(P1,W2, strides = [1,1,1,1], padding = 'SAME')
# RELU
A2 = tf.nn.relu(Z2)
# MAXPOOL: window 4x4, stride 4, padding 'SAME'
P2 = tf.nn.max_pool(A2, ksize = [1,4,4,1], strides = [1,4,4,1], padding = 'SAME')
# FLATTEN
P2 = tf.contrib.layers.flatten(P2)
# FULLY-CONNECTED without non-linear activation function (not not call softmax).
# 6 neurons in output layer. Hint: one of the arguments should be "activation_fn=None"
Z3 = tf.contrib.layers.fully_connected(P2, num_outputs = 6, activation_fn=None)
### END CODE HERE ###
return Z3
tf.reset_default_graph()
with tf.Session() as sess:
np.random.seed(1)
X, Y = create_placeholders(64, 64, 3, 6)
parameters = initialize_parameters()
Z3 = forward_propagation(X, parameters)
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init)
a = sess.run(Z3, {X: np.random.randn(2,64,64,3), Y: np.random.randn(2,6)})
print("Z3 = " + str(a))
输出结果为
Z3 = [[-0.44670227 -1.57208765 -1.53049231 -2.31013036 -1.29104376 0.46852064]
[-0.17601591 -1.57972014 -1.4737016 -2.61672091 -1.00810647 0.5747785 ]]
1.4 - 计算成本
实现下面的计算成本函数。你可能会发现这两个函数很有用:
tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits = Z3, labels =Y):计算softmax熵损失。这个函数既计算softmax激活函数,也计算由此产生的损失。你可以在这里查看完整的文档。tf.reduce_mean:计算张量各个维度元素的平均值。用这个公式把所有例子的损失加起来,得到总成本。你可以在这里查看完整的文档。
练习:使用上面的函数计算下面的成本。
# GRADED FUNCTION: compute_cost
def compute_cost(Z3, Y):
"""
Computes the cost
Arguments:
Z3 -- output of forward propagation (output of the last LINEAR unit), of shape (6, number of examples)
Y -- "true" labels vector placeholder, same shape as Z3
Returns:
cost - Tensor of the cost function
"""
### START CODE HERE ### (1 line of code)
cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=Z3, labels=Y))
### END CODE HERE ###
return cost
tf.reset_default_graph()
with tf.Session() as sess:
np.random.seed(1)
X, Y = create_placeholders(64, 64, 3, 6)
parameters = initialize_parameters()
Z3 = forward_propagation(X, parameters)
cost = compute_cost(Z3, Y)
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init)
a = sess.run(cost, {X: np.random.randn(4,64,64,3), Y: np.random.randn(4,6)})
print("cost = " + str(a))
输出
cost = 2.91034
1.5 - 模型
最后,您将合并上面实现的helper函数来构建模型。您将在SIGNS数据集上训练它。
你已经在课程2实现了random_mini_batches()。记住,这个函数返回一个小批量的列表。
练习:完成下列功能。
以下模型应该:
- 创建占位符
- 初始化参数
- 向前传播
- 计算出成本
- 创建一个优化器
最后,您将创建一个会话并为num_epochs运行一个for循环,获取小批量,然后为每个小批量优化函数。
# GRADED FUNCTION: model
def model(X_train, Y_train, X_test, Y_test, learning_rate = 0.009,
num_epochs = 100, minibatch_size = 64, print_cost = True):
"""
Implements a three-layer ConvNet in Tensorflow:
CONV2D -> RELU -> MAXPOOL -> CONV2D -> RELU -> MAXPOOL -> FLATTEN -> FULLYCONNECTED
Arguments:
X_train -- training set, of shape (None, 64, 64, 3)
Y_train -- test set, of shape (None, n_y = 6)
X_test -- training set, of shape (None, 64, 64, 3)
Y_test -- test set, of shape (None, n_y = 6)
learning_rate -- learning rate of the optimization
num_epochs -- number of epochs of the optimization loop
minibatch_size -- size of a minibatch
print_cost -- True to print the cost every 100 epochs
Returns:
train_accuracy -- real number, accuracy on the train set (X_train)
test_accuracy -- real number, testing accuracy on the test set (X_test)
parameters -- parameters learnt by the model. They can then be used to predict.
"""
ops.reset_default_graph() # to be able to rerun the model without overwriting tf variables
tf.set_random_seed(1) # to keep results consistent (tensorflow seed)
seed = 3 # to keep results consistent (numpy seed)
(m, n_H0, n_W0, n_C0) = X_train.shape
n_y = Y_train.shape[1]
costs = [] # To keep track of the cost
# Create Placeholders of the correct shape
### START CODE HERE ### (1 line)
X, Y = create_placeholders(n_H0, n_W0, n_C0, n_y)
### END CODE HERE ###
# Initialize parameters
### START CODE HERE ### (1 line)
parameters = initialize_parameters()
### END CODE HERE ###
# Forward propagation: Build the forward propagation in the tensorflow graph
### START CODE HERE ### (1 line)
Z3 = forward_propagation(X, parameters)
### END CODE HERE ###
# Cost function: Add cost function to tensorflow graph
### START CODE HERE ### (1 line)
cost = compute_cost(Z3, Y)
### END CODE HERE ###
# Backpropagation: Define the tensorflow optimizer. Use an AdamOptimizer that minimizes the cost.
### START CODE HERE ### (1 line)
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=learning_rate).minimize(cost)
### END CODE HERE ###
# Initialize all the variables globally
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
# Start the session to compute the tensorflow graph
with tf.Session() as sess:
# Run the initialization
sess.run(init)
# Do the training loop
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
minibatch_cost = 0.
num_minibatches = int(m / minibatch_size) # number of minibatches of size minibatch_size in the train set
seed = seed + 1
minibatches = random_mini_batches(X_train, Y_train, minibatch_size, seed)
for minibatch in minibatches:
# Select a minibatch
(minibatch_X, minibatch_Y) = minibatch
# IMPORTANT: The line that runs the graph on a minibatch.
# Run the session to execute the optimizer and the cost, the feedict should contain a minibatch for (X,Y).
### START CODE HERE ### (1 line)
_ , temp_cost = sess.run([optimizer, cost], feed_dict={X:minibatch_X, Y:minibatch_Y})
### END CODE HERE ###
minibatch_cost += temp_cost / num_minibatches
# Print the cost every epoch
if print_cost == True and epoch % 5 == 0:
print ("Cost after epoch %i: %f" % (epoch, minibatch_cost))
if print_cost == True and epoch % 1 == 0:
costs.append(minibatch_cost)
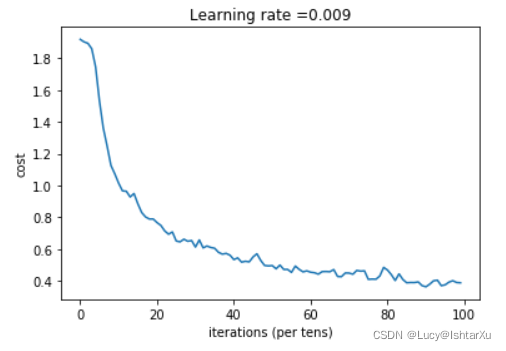
# plot the cost
plt.plot(np.squeeze(costs))
plt.ylabel('cost')
plt.xlabel('iterations (per tens)')
plt.title("Learning rate =" + str(learning_rate))
plt.show()
# Calculate the correct predictions
predict_op = tf.argmax(Z3, 1)
correct_prediction = tf.equal(predict_op, tf.argmax(Y, 1))
# Calculate accuracy on the test set
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, "float"))
print(accuracy)
train_accuracy = accuracy.eval({X: X_train, Y: Y_train})
test_accuracy = accuracy.eval({X: X_test, Y: Y_test})
print("Train Accuracy:", train_accuracy)
print("Test Accuracy:", test_accuracy)
return train_accuracy, test_accuracy, parameters
_, _, parameters = model(X_train, Y_train, X_test, Y_test)
输出结果为
Cost after epoch 0: 1.917920
Cost after epoch 5: 1.532475
Cost after epoch 10: 1.014804
Cost after epoch 15: 0.885137
Cost after epoch 20: 0.766963
Cost after epoch 25: 0.651208
Cost after epoch 30: 0.613356
Cost after epoch 35: 0.605931
Cost after epoch 40: 0.534713
Cost after epoch 45: 0.551402
Cost after epoch 50: 0.496976
Cost after epoch 55: 0.454438
Cost after epoch 60: 0.455496
Cost after epoch 65: 0.458359
Cost after epoch 70: 0.450040
Cost after epoch 75: 0.410687
Cost after epoch 80: 0.469005
Cost after epoch 85: 0.389253
Cost after epoch 90: 0.363808
Cost after epoch 95: 0.376132
Tensor(“Mean_1:0”, shape=(), dtype=float32)
恭喜你!您已经完成了作业,并建立了一个模型,识别手语的准确性接近80%的测试集。如果您愿意,可以自由地进一步使用这个数据集。实际上,您可以通过花更多的时间调整超参数或使用正则化(因为该模型显然具有很高的方差)来提高其准确性。
再一次,为你的工作竖起大拇指!
fname = "images/thumbs_up.jpg"
image = np.array(ndimage.imread(fname, flatten=False))
my_image = scipy.misc.imresize(image, size=(64,64))
plt.imshow(my_image)

更多推荐
 已为社区贡献2条内容
已为社区贡献2条内容









所有评论(0)