多模态大模型目标检测——数据集制作
摘要:本研究探讨了基于Qwen2-VL-2B大模型的道路病害检测方法,采用RDD2022数据集进行微调。针对VOC格式数据预处理问题,提出坐标归一化方法(0-1000区间),并开发数据处理流程:1)筛选特定病害类别(如网裂D20);2)解析XML提取坐标信息;3)绘制带检测框的验证图像。通过Python脚本实现数据格式转换,生成包含归一化坐标和病害类别的JSON文件,最终形成符合大模型微调要求的结
通过对大模型进行微调实现道路病害进行检测,在进行微调之前需要对数据进行一系列处理,使其满足微调格式。
采用RDD2022数据集,原数据集为VOC格式,仅包含图像数据与XML数据,为了使其满足微调格式,需要进行处理。
首先需要提取出图像名称、病害所属种类,以及对应的病害坐标。
在实验中利用Qwen2-VL-2B进行微调,图片中的病害坐标点需要归一化到1~1000,如果输入图像超过该模型的最大分辨率会对输入图像进行resize,这将导致输入坐标不准。
坐标归一化
def normalize_bbox(solution, width, height, scale=1000):
x1, y1, x2, y2 = solution
norm_x1 = int((x1 / width) * scale)
norm_y1 = int((y1 / height) * scale)
norm_x2 = int((x2 / width) * scale)
norm_y2 = int((y2 / height) * scale)
return [norm_x1, norm_y1, norm_x2, norm_y2]
RDD2022部分数据坐标点为小数,上面的代码需要进行稍微修改,修改为能进行double计算的。
xml类别选择
根据目标任务,挑选需要的目标类,并且根据xml中的坐标绘制坐标转变后的带有检测框的图像,方便后续进行评价指标的计算,这里以D20类别进行演示
"""挑选出RDD图像中D20类别的数据,即网裂的数据(仅包含网裂),保存原图,画出bbox的图以及相应xml文件,一共挑出2734张图像"""
import os
import cv2
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import shutil
# 设置文件夹路径
base_folder = r"E:\BaiduNetdiskDownload" # 主文件夹,包含子文件夹和图像、XML文件
image_folder = os.path.join(base_folder, "IMG") # 图像文件夹路径
xml_folder = os.path.join(base_folder, "XML") # XML文件夹路径
save_image_folder = "WaterFilled/images" # 保存原图像文件夹
save_bbox_folder = "WaterFilled/groundTruth" # 保存带检测框的图像文件夹
save_xml_folder = "WaterFilled/xmls"
# 特定的类别名称
target_class = "pothole"
# 创建保存文件夹
os.makedirs(save_image_folder, exist_ok=True)
os.makedirs(save_bbox_folder, exist_ok=True)
os.makedirs(save_xml_folder, exist_ok=True)
def parse_xml(xml_file):
"""解析XML文件,返回图像文件名和物体信息"""
tree = ET.parse(xml_file)
root = tree.getroot()
image_filename = root.find('filename').text
objects = []
for obj in root.findall('object'):
name = obj.find('name').text
bndbox = obj.find('bndbox')
# xmin = int(round(float(bndbox.find('xmin').text))) # 方便浮点数计算
# ymin = int(round(float(bndbox.find('ymin').text)))
# xmax = int(round(float(bndbox.find('xmax').text)))
# ymax = int(round(float(bndbox.find('ymax').text)))
xmin = int(bndbox.find('xmin').text)
ymin = int(bndbox.find('ymin').text)
xmax = int(bndbox.find('xmax').text)
ymax = int(bndbox.find('ymax').text)
objects.append((name, xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax))
return image_filename, objects
def process_image(xml_file):
"""处理图像,根据XML文件中的注释进行筛选和绘制检测框"""
image_filename, objects = parse_xml(xml_file)
image_path = os.path.join(image_folder, image_filename)
if not os.path.exists(image_path):
print(f"图像文件 {image_filename} 不存在")
return
# 加载图像
image = cv2.imread(image_path)
# 过滤出目标类别的物体
target_objects = [obj for obj in objects if obj[0] == target_class]
# 如果没有目标类别的物体,跳过
if (len(target_objects) != len(objects)) or (len(target_objects) == 0):
print(f"图像 {image_filename} 中没有只包含目标类别 {target_class},跳过该图像")
return
# 保存原图
save_path = os.path.join(save_image_folder, image_filename)
shutil.copy(image_path, save_path)
print(f"保存原图像: {save_path}")
# 绘制检测框并保存带框图像
for obj in target_objects:
_, xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax = obj
# 绘制绿色框
cv2.rectangle(image, (xmin, ymin), (xmax, ymax), (0, 0, 255), 2)
# 保存带检测框的图像
bbox_save_path = os.path.join(save_bbox_folder, image_filename)
cv2.imwrite(bbox_save_path, image)
print(f"保存带检测框的图像: {bbox_save_path}")
# 复制XML文件到目标文件夹
xml_save_path = os.path.join(save_xml_folder, os.path.basename(xml_file))
shutil.copy(xml_file, xml_save_path)
print(f"保存过滤后的XML文件: {xml_save_path}")
def process_annotations():
"""处理annotations文件夹中的所有XML文件,筛选并保存符合条件的图像"""
for xml_file in os.listdir(xml_folder):
if xml_file.endswith(".xml"):
xml_file_path = os.path.join(xml_folder, xml_file)
process_image(xml_file_path)
# 开始处理
process_annotations()
json文件
通过上述处理已经获取了我们需要的类别,下一步需要将选取出来的类别转换为qwen2-VL能够识别的格式。处理后的数据格式如下图所示。

将' '中的内容换为带检测目标类的类名,并读出该张图像中的所有病害的病害坐标(转换后的坐标)。我们将筛选出的xml文件通过坐标转化、内容拼接,组成一个json文件,格式如下图所示。
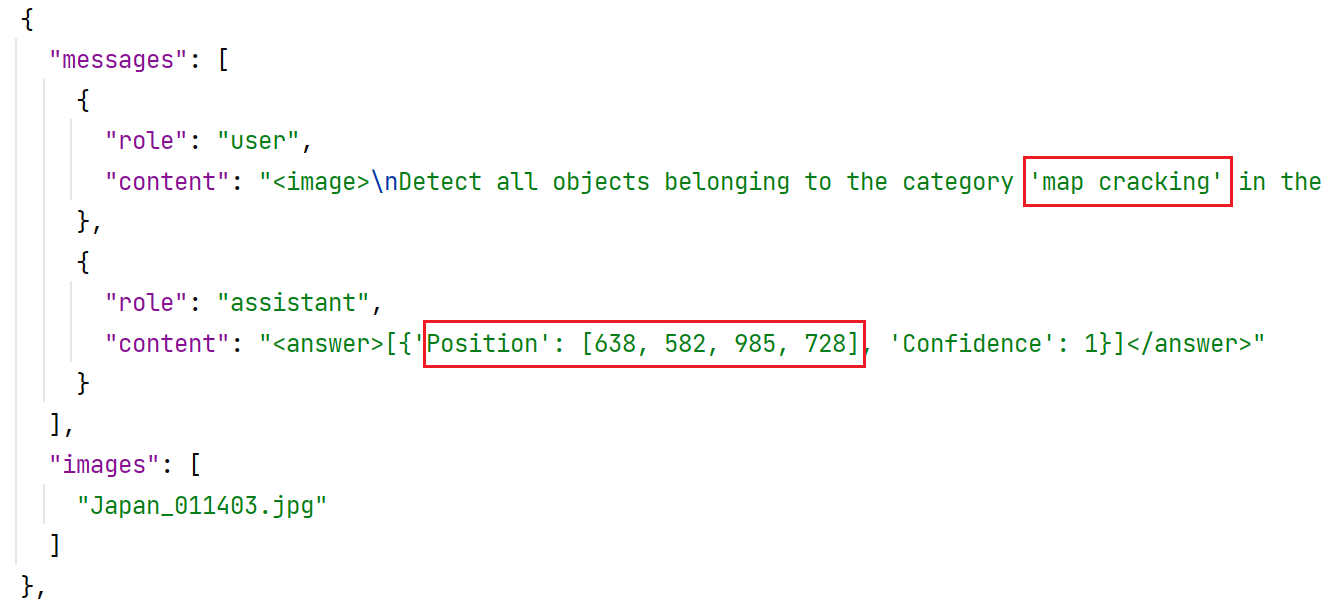
处理代码如下,代码需要根据实际使用的文件夹路径与检测类别进行修改。
import os
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import json
from pathlib import Path
import random
from typing import List, Dict, Union
def safe_get_text(element: ET.Element, tag: str, default: str = "") -> str:
"""获取XML元素的文本内容"""
target = element.find(tag)
return target.text.strip() if (target is not None and target.text) else default
def normalization(xmin: float, ymin: float, xmax: float, ymax: float,
width: float, height: float) -> List[int]:
"""坐标归一化处理(支持浮点数输入)"""
return [
int(round((xmin / width) * 1000)), # round函数对数字进行四舍五入,默认是四舍六入五取偶
int(round((ymin / height) * 1000)),
int(round((xmax / width) * 1000)),
int(round((ymax / height) * 1000))
]
def parse_coordinate(box: ET.Element) -> Dict[str, float]:
"""解析边界框坐标并验证有效性"""
coords = {}
for coord in ['xmin', 'ymin', 'xmax', 'ymax']:
text = safe_get_text(box, coord, "0")
try:
coords[coord] = float(text)
except ValueError:
raise ValueError(f"无效坐标值: {coord}={text}")
return coords
def generate_answer_content(boxes: List[List[int]]) -> str:
"""生成无转义字符的answer内容"""
if not boxes:
return "<answer>No Objects</answer>"
items = []
for box in boxes:
pos_str = f"[{box[0]}, {box[1]}, {box[2]}, {box[3]}]"
items.append(f"{{'Position': {pos_str}, 'Confidence': 1}}")
return f"<answer>[{', '.join(items)}]</answer>"
def process_xml_file(xml_path: str, target_class: str) -> Union[Dict, None]:
# def process_xml_file(xml_path: str) -> Union[Dict, None]:
"""处理单个XML文件"""
try:
# 解析XML结构
tree = ET.parse(xml_path)
root = tree.getroot()
# 解析元数据
filename = safe_get_text(root, "filename", "unknown.jpg")
size = root.find("size")
# 获取图像尺寸
try:
width = float(safe_get_text(size, "width", "0"))
height = float(safe_get_text(size, "height", "0"))
if width <= 0 or height <= 0:
raise ValueError("无效的尺寸值")
except (TypeError, ValueError) as e:
print(f"[{xml_path}] 尺寸解析错误: {str(e)}")
return None
# 解析目标物体
normalized_boxes = []
for obj in root.findall("object"):
if safe_get_text(obj, "name") != target_class: #xml_class:
continue
# 坐标解析
box = obj.find("bndbox")
if box is None:
continue
try:
coords = parse_coordinate(box)
norm_box = normalization(
coords['xmin'], coords['ymin'],
coords['xmax'], coords['ymax'],
width, height
)
normalized_boxes.append(norm_box)
except Exception as e:
print(f"[{xml_path}] 坐标处理错误: {str(e)}")
continue
# 构建用户消息
user_content = f"""<image>
Detect all objects belonging to the category '{target_class}' in the image, and provide the bounding boxes (between 0 and 1000, integer) and confidence (between 0 and 1, with two decimal places).
If no object belonging to the category '{target_class}' in the image, return 'No Objects'. Output the thinking process in <think> </think> and final answer in <answer> </answer> tags.The output answer format should be as follows:
<think> ... </think> <answer>[{{'Position': [x1, y1, x2, y2], 'Confidence': number}}, ...]</answer>
Please strictly follow the format."""
# 生成最终结果
return {
"messages": [
{"role": "user", "content": user_content},
{"role": "assistant", "content": generate_answer_content(normalized_boxes)}
],
"images": [filename]
}
except ET.ParseError:
print(f"[{xml_path}] XML格式错误")
return None
except Exception as e:
print(f"[{xml_path}] 处理失败: {str(e)}")
return None
def batch_convert_xml_to_json(input_dir: str, output_path: str, target_class):
"""批量转换XML文件夹"""
valid_results = []
# 遍历XML文件
for filename in os.listdir(input_dir):
if not filename.lower().endswith(".xml"):
continue
xml_path = os.path.join(input_dir, filename)
if result := process_xml_file(xml_path, target_class):
valid_results.append(result)
file_path = Path(output_path)
# 写入JSON文件
if not file_path.exists():
file_path.touch()
print(f"{output_path}已创建")
with open(output_path, "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
json.dump(
valid_results,
f,
indent=2,
ensure_ascii=False,
separators=(",", ": ")
)
print(f"转换完成,有效文件数: {len(valid_results)},输出路径: {os.path.abspath(output_path)}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
batch_convert_xml_to_json(
input_dir=r"E:\BaiduNetdiskDownload\train_xml",
output_path="../processedData/json/train.json",
target_class="pothole"
)
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容








所有评论(0)