pyspark机器学习
Introduction:
简介 :
PySpark is the Python API written in python to support Apache Spark. Apache Spark is a distributed framework that can handle Big Data analysis. Spark is written in Scala and can be integrated with Python, Scala, Java, R, SQL languages. Spark is basically a computational engine, that works with huge sets of data by processing them in parallel and batch systems. When you down load spark binaries there will separate folders to support above langauges.
PySpark是用python编写的Python API,用于支持Apache Spark。 Apache Spark是一个分布式框架,可以处理大数据分析。 Spark用Scala编写,可以与Python,Scala,Java,R,SQL语言集成。 Spark基本上是一个计算引擎,通过在并行和批处理系统中处理大量数据来处理它们。 当您下载spark二进制文件时,将有单独的文件夹来支持上述语言。
There are basically two major types of algorithms — transformers : Transforms work with the input datasets and modify it to output datasets using a transform().
基本上有两种主要的算法类型-转换器:转换与输入数据集一起使用,并使用transform()将其修改为输出数据集。
Estimators are the algorithms that take input datasets and produces a trained output model using fit().
估计器是采用输入数据集并使用fit()生成训练后的输出模型的算法。
In this section, I will be showing the machine learning implementation using Spark and Python. I will be focusing here basic ML algorithm Linear Regression implemented in the context of Spark. The program has been executed in the standalone server.
在本节中,我将展示使用Spark和Python的机器学习实现。 我将在这里重点介绍在Spark环境中实现的基本ML算法线性回归。 该程序已在独立服务器中执行。
First, import the libraries as shown below. And it is the most important to give the path of Spark binaries present in your system. Otherwise, you may face issues in executing codes.
首先,如下所示导入库。 给出系统中存在的Spark二进制文件的路径是最重要的。 否则,您可能会在执行代码时遇到问题。
Spark Session :
火花会议 :
This is the entry point to the programming spark with Dataframe API & dataset. That allows you to perform various tasks using spark. spark context, hive context, SQL context, now all of it is encapsulated in the session. Before spark 2.0, sparkContext was used to access all spark functionality. The spark driver program uses sparkContext to connect to the cluster through a resource manager. sparkConf creates the sparkContext object, which stores configuration parameter like appName (to identify your spark driver), application, number of core, and memory size of executor running on the worker node. After spark 2.0 onwards these two features are encapsulated in spark session. So each time you want to perform tasks using spark you need to create a session and after execution, you must end the session.
这是使用Dataframe API和数据集进行编程火花的切入点。 这使您可以使用spark执行各种任务。 spark上下文,hive上下文,SQL上下文,现在所有这些都封装在会话中。 在spark 2.0之前,sparkContext用于访问所有spark功能。 Spark驱动程序使用sparkContext通过资源管理器连接到集群。 sparkConf创建sparkContext对象,该对象存储配置参数,例如appName(用于标识您的Spark驱动程序),应用程序,内核数以及在工作程序节点上运行的执行程序的内存大小。 从spark 2.0开始,这两个功能被封装在spark会话中。 因此,每次您要使用spark执行任务时,都需要创建一个会话,执行之后,必须结束该会话。
Now read the data set using read.csv() you can allow the spark to read the dataset and to execute when it is required. Here I have used one real estate dataset used.
现在使用read.csv()读取数据集,您可以允许spark读取数据集并在需要时执行。 在这里,我使用了一个真实的房地产数据集 。
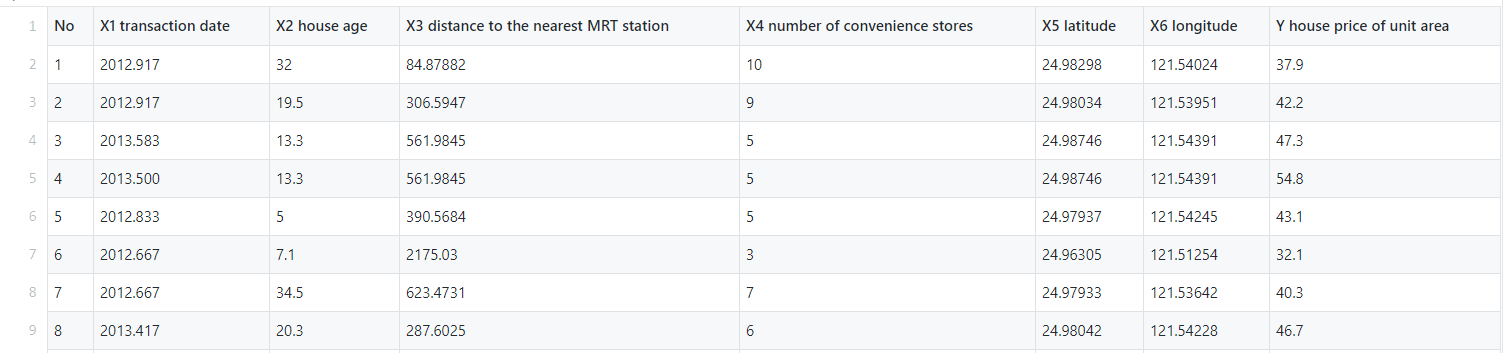
Here you can notice the columns such as No and X1 transaction date are independent of the price of the house and the transaction date is not properly given in the datasets. so we will drop those columns
在这里,您会注意到诸如No和X1交易日期之类的列与房屋价格无关,并且在数据集中未正确给出交易日期。 所以我们将删除这些列
colm = ['No','X1 transaction date']
df = dataset.select([column for column in dataset.columns if column not in colm])
there is a cool spark syntax is there to do that. if you apply a list comprehension in select() you will get the required data frame. This data frame is different from the Pandas data frame. Well, it is related to the objects created in spark and pandas.
有一个很酷的火花语法可以做到这一点。 如果在select()中应用列表推导,则将获得所需的数据框。 此数据帧不同于熊猫数据帧。 好吧,它与在spark和pandas中创建的对象有关。
Spark data frame is distributed hence you will get the benefit of parallel processing and speed of processing while handling large datasets.
Spark数据帧是分布式的,因此在处理大型数据集时将获得并行处理和处理速度的优势。
Spark assures fault tolerance. So if your data processing got interrupted/failed in between processing then spark can regenerate the failed result set from the lineage.
火花确保容错能力。 因此,如果您的数据处理在两次处理之间被中断/失败,那么spark可以从沿袭中重新生成失败的结果集。
df.printSchema() #output root
|-- X2 house age: string (nullable = true)
|-- X3 distance to the nearest MRT station: string (nullable = true)
|-- X4 number of convenience stores: string (nullable = true)
|-- X5 latitude: string (nullable = true)
|-- X6 longitude: string (nullable = true)
|-- Y house price of unit area: string (nullable = true)
If you look at the schema of the dataset, it is in the string format. Lets typecast to float.
如果查看数据集的架构,则该格式为字符串格式。 让类型转换浮动。
from pyspark.sql.functions import col df = df.select(*(col(c).cast('float').alias(c) for c in df.columns))
Let’s check for null values.
让我们检查一下空值。
df.select([count(when(col(c).isNull(), c)).alias(c) for c in df.columns]).show()
Great! there are no null values present. But the column names are a bit longer. So we will now replace those with our own custom names. For renaming the column name there are several techniques that are there, I have used reduce () to do that. You can perform in another way.
大! 没有空值。 但是列名要长一些。 因此,我们现在将其替换为我们自己的自定义名称。 为了重命名列名,有几种技术,我使用reduce()来做到这一点。 您可以用其他方式执行。
from functools import reduce
oldColumns = df.schema.names
newColumns = ['Age','Distance_2_MRT','Stores','Latitude','Longitude','Price']
df = reduce( lambda df, idx: df.withColumnRenamed(oldColumns[idx], newColumns[idx]),range(len(oldColumns)), df)
Try different techniques and let me know as well.
尝试不同的技术,并让我知道。
Sharing is caring : )
分享很贴心:)
Now we will do split to get Features and Label columns.
现在,我们将进行拆分以获取功能和标签列。
VectorAssembler:
VectorAssembler:
VectorAssembler is a transformer that combines a given list of columns into a single vector column. It is useful for combining raw features and features generated by different feature transformers into a single feature vector, in order to train ML models.
VectorAssembler是一种转换器,它将给定的列列表组合为单个向量列。 这对于将原始特征和由不同特征转换器生成的特征组合到单个特征向量中很有用,以训练ML模型。
from pyspark.ml.feature import VectorAssembler
#let's assemble our features together using vectorAssembler
assembler = VectorAssembler(
inputCols=features.columns,
outputCol="features")
output = assembler.transform(df).select('features','Price')
This will transform the target and features columns. Now we will split it into train and test dataset.
这将转换目标和特征列。 现在,我们将其分为训练和测试数据集。
train,test = output.randomSplit([0.75, 0.25])
Let’s now apply a Linear Regression model
现在让我们应用线性回归模型
from pyspark.ml.regression import LinearRegression
lin_reg = LinearRegression(featuresCol = 'features', labelCol='Price')
linear_model = lin_reg.fit(train) print("Coefficients: " + str(linear_model.coefficients))
print(" \n Intercept: " + str(linear_model.intercept)) #Output
Coefficients: [-0.2845380180805475,-0.004727311005402087,1.187968326885585,201.55230488460887,-43.50846789357342]
Intercept: 298.6774040798928
The coefficients for each column and Intercept we got.
我们获得的每一列和截距的系数。
trainSummary = linear_model.summary
print("RMSE: %f " % trainSummary.rootMeanSquaredError)
print(" \n r2: %f " % trainSummary.r2) #Output
RMSE: 9.110080
r2: 0.554706
For testing dataset
用于测试数据集
from pyspark.sql.functions import abs
predictions = linear_model.transform(test)
x =((predictions['Price']-predictions['prediction'])/predictions['Price'])*100
predictions = predictions.withColumn('Accuracy',abs(x))
predictions.select("prediction","Price","Accuracy","features").show()
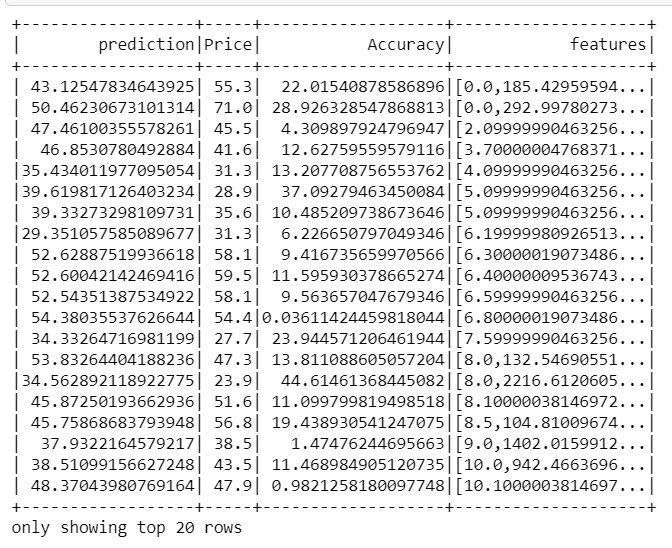
r — square value for the test dataset
r —测试数据集的平方值
from pyspark.ml.evaluation import RegressionEvaluator pred_evaluator = RegressionEvaluator(predictionCol="prediction", \
labelCol="Price",metricName="r2")
print("R Squared (R2) on test data = %g " % pred_evaluator.evaluate(predictions)) #output
R Squared (R2) on test data = 0.610204
Let’s now check for adjusted R square.
现在让我们检查调整后的R平方。
Adjusted R — square:
调整后的R —平方:
The adjusted R-squared is a modified version of R-squared that has been adjusted for the number of predictors in the model. The adjusted R-squared increases only if the new term improves the model more than would be expected by chance. It decreases when a predictor improves the model by less than expected. We use Adjusted R2 value which penalizes excessive use of such features that do not correlate with the output data.
调整后的R平方是R平方修饰版本,已调整为在模型中的预测变量数。 仅当新项对模型的改进超出偶然的预期时, 调整后的R平方才会增加。 当预测变量对模型的改进少于预期时,它会减少。 我们使用调整后的R2值,这会惩罚过度使用与输出数据不相关的功能。
r2 = trainSummary.r2
n = df.count()
p = len(df.columns)
adjusted_r2 = 1-(1-r2)*(n-1)/(n-p-1)
We got adjusted r squared value 0.54 for training and testing.
我们为训练和测试获得了调整后的r平方值0.54。
Let’s now explore more on the LinearRegression() in the spark.
现在,让我们进一步探讨LinearRegression()。
lin_reg = LinearRegression(featuresCol = 'features', labelCol='Price',maxIter=50, regParam=0.12, elasticNetParam=0.2)
linear_model = lin_reg.fit(train)
Here you can apply Lasso, Ridge, Elastic net regularization, alpha values you can modify. There is a very good article on these concepts. This is a shared repository for Learning Apache Spark Notes. This shared repository mainly contains the self-learning and self-teaching notes from Wenqiang during his IMA Data Science Fellowship. Thanks to George Feng, A senior data scientist at ML Lab.
您可以在此处应用套索,山脊,弹性网正则化,可以修改的Alpha值。 关于这些概念的文章非常好。 这是用于学习Apache Spark Notes的共享存储库。 该共享存储库主要包含Wenqiang在IMA数据科学奖学金期间的自学和自学笔记。 感谢ML Lab的资深数据科学家George Feng 。
I will be sharing other spark implemented ML algorithms in future stories.
我将在以后的故事中分享其他使用Spark实现的ML算法。
For suggestions, I will be available on LinkedIn , Gmail , Twiiter &follow my work at GitHub.
对于建议,我可以在 LinkedIn , Gmail , Twiiter 上 找到 , 并 在 GitHub上 关注我的工作 。
翻译自: https://towardsdatascience.com/machine-learning-linear-regression-using-pyspark-9d5d5c772b42
pyspark机器学习








 已为社区贡献3条内容
已为社区贡献3条内容

所有评论(0)